Embark on a journey to optimize your workspace and elevate your productivity with a dual monitor setup. This comprehensive guide details the essential steps, from choosing the right monitors to configuring display settings, ensuring a seamless transition to a more efficient and visually engaging experience. Understanding the benefits of dual monitors, including enhanced multitasking and improved visual clarity, is paramount to maximizing your output.
This guide will walk you through selecting the ideal monitors for your needs, considering factors like resolution, refresh rate, and size. It will also explain the different connection types, providing a detailed comparison of various display ports. Crucially, we’ll delve into configuring the display settings within your operating system, covering everything from resolution adjustments to arranging your monitors for optimal use.
Troubleshooting common issues is also covered, equipping you with the tools to resolve potential problems.
Introduction to Dual Monitor Setup

Dual monitors offer a significant enhancement to the user experience, providing a more immersive and productive work environment. By extending the desktop or mirroring the display, users can manage multiple applications, windows, and tasks simultaneously, increasing efficiency and reducing visual fatigue. This expanded workspace optimizes workflow for various activities, from graphic design and video editing to programming and general office work.Dual monitor setups are highly adaptable to individual needs and preferences.
They can significantly enhance productivity and comfort for users by providing a larger workspace and improved visual organization. Different configurations cater to specific use cases, allowing users to tailor their setup to maximize their efficiency.
Dual Monitor Setup Benefits
Dual monitors offer several benefits. Increased screen real estate allows users to run multiple applications simultaneously without overlapping windows, improving workflow and efficiency. This is particularly helpful for tasks requiring multiple windows or applications, such as editing photos or videos, coding, or performing research. Users also experience a more immersive and comfortable visual experience.
Types of Dual Monitor Setups
Dual monitor setups can be configured in several ways. Mirroring displays the same image on both screens, which is useful for presentations and watching videos. Extended displays offer separate workspaces on each monitor, allowing users to have multiple applications open and visible simultaneously. This is commonly used for increased productivity and multitasking.
Hardware Requirements
Certain hardware components are necessary for a successful dual monitor setup. A graphics card with sufficient video outputs is crucial to support two monitors. The graphics card must have the necessary ports (e.g., DisplayPort, HDMI, DVI) to connect the monitors. The specific requirements depend on the type of monitor and video output. Users should ensure that the graphics card and monitor ports are compatible.
Comparison of Mirroring and Extended Desktop Modes
Different configurations of dual monitor setups cater to various needs. The following table illustrates the key differences between mirroring and extended desktop modes.
| Feature | Mirroring | Extended Desktop |
|---|---|---|
| Display | Same image on both screens | Different images on each screen |
| Resolution | Same as single monitor | Different resolution on each screen (or same) |
| Use Case | Presentations, watching videos | Multiple tasks, productivity |
Mirroring presents a consistent display on both screens, ideal for showcasing information or viewing a video. Extended desktop offers separate workspaces on each screen, providing ample room for running multiple applications simultaneously, maximizing productivity and multitasking.
Choosing the Right Monitors
Selecting appropriate monitors is crucial for a productive and enjoyable dual-monitor setup. The right monitors will enhance your visual experience and streamline your workflow, ensuring a comfortable and efficient workspace. Careful consideration of various factors like resolution, refresh rate, and monitor type is essential to make the best choice.Selecting monitors that meet your needs and preferences is vital.
A poor choice can lead to eye strain, reduced productivity, and an overall less satisfying experience. Understanding the different monitor technologies and their associated advantages and disadvantages is paramount to making an informed decision.
Resolution, Refresh Rate, and Size
The resolution, refresh rate, and size of your monitors directly impact image quality and user experience. High resolution provides sharper, more detailed images, perfect for tasks requiring precision. A higher refresh rate results in smoother motion, crucial for activities like gaming or video editing. Monitor size is important for comfort and workspace optimization. A larger monitor is more accommodating for tasks requiring a broader view, but a smaller monitor might be preferable for space-constrained setups.
For instance, a 4K resolution monitor is ideal for professional graphic design or video editing, offering exceptionally detailed images. A higher refresh rate is beneficial for gaming, as it minimizes motion blur, resulting in a smoother and more responsive experience.
Monitor Technologies
Different monitor technologies offer varying characteristics. Understanding these differences will help you choose the best monitors for your specific needs. The most common types include LCD, LED, and OLED, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Comparison of Monitor Technologies
| Technology | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| LCD | Affordable, widely available, and generally reliable. They offer a wide range of sizes and resolutions to accommodate various needs. | Lower color accuracy compared to other technologies, and slower response times, potentially leading to motion blur in fast-paced applications. |
| LED | Brighter and thinner than LCD monitors, with improved energy efficiency. LED backlighting provides a more vibrant and accurate color representation. | Can sometimes exhibit backlight bleed, where light leaks from the backlight, causing uneven illumination across the screen. This can affect the visual quality, especially in dark scenes. |
| OLED | Offers exceptional color accuracy, producing incredibly deep blacks and vibrant colors. OLEDs have significantly faster response times, leading to smoother motion in dynamic content. | Higher cost compared to LCD and LED monitors. Potential for burn-in issues, where static images can remain imprinted on the screen over time, though this is less of a concern with modern panels. |
Connecting the Monitors

Connecting your monitors to your computer is a crucial step in setting up a dual monitor setup. Proper connections ensure a stable and seamless display experience. Understanding the different types of display ports and how to connect them correctly will prevent frustrating issues and allow you to enjoy the benefits of a dual monitor setup.
Display Port Types
Various display ports facilitate the connection between monitors and computers. Familiarizing yourself with these types will help you choose the right cables and ensure compatibility.
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface): HDMI is a versatile digital audio/video interface widely used for connecting various devices, including televisions, projectors, and monitors. It transmits both video and audio signals over a single cable, making it a popular choice for its convenience and compatibility.
- DisplayPort: DisplayPort is a digital interface specifically designed for high-resolution displays. It offers superior bandwidth compared to HDMI, enabling higher refresh rates and resolutions, essential for demanding applications like gaming or professional design work. It’s frequently found on modern graphics cards and laptops.
- VGA (Video Graphics Array): VGA is an older analog video interface. While still supported by some older devices, its limitations in resolution and bandwidth make it less suitable for modern high-resolution displays. VGA is primarily found on older computers and some peripherals.
Connecting Monitors to a Computer
Connecting monitors involves careful consideration of the available ports on both the computer and the monitors. Correctly matching the ports is vital for a smooth setup.
- Using HDMI: If your computer and monitors support HDMI, connect the HDMI cable from the computer’s HDMI port to the corresponding port on the monitor. Ensure the correct cable is used, as different HDMI versions have different capabilities. For instance, an HDMI 2.0 cable is sufficient for most standard displays.
- Using DisplayPort: Connect the DisplayPort cable from the computer’s DisplayPort port to the corresponding port on the monitor. Like HDMI, different DisplayPort versions exist, and you should choose the appropriate cable to match the resolution and refresh rate requirements of your setup.
- Using VGA: Connect the VGA cable from the computer’s VGA port to the corresponding port on the monitor. Note that VGA is a legacy technology and might not support high resolutions or refresh rates.
Dual Monitor Setup Procedure
Setting up dual monitors involves connecting both monitors to the computer. The following steps provide a clear guide.
- Connect Monitor 1: Connect one monitor to the computer using the appropriate cable and port. Ensure the monitor is turned on.
- Connect Monitor 2: Connect the second monitor to the computer using the appropriate cable and port. Again, ensure the monitor is turned on.
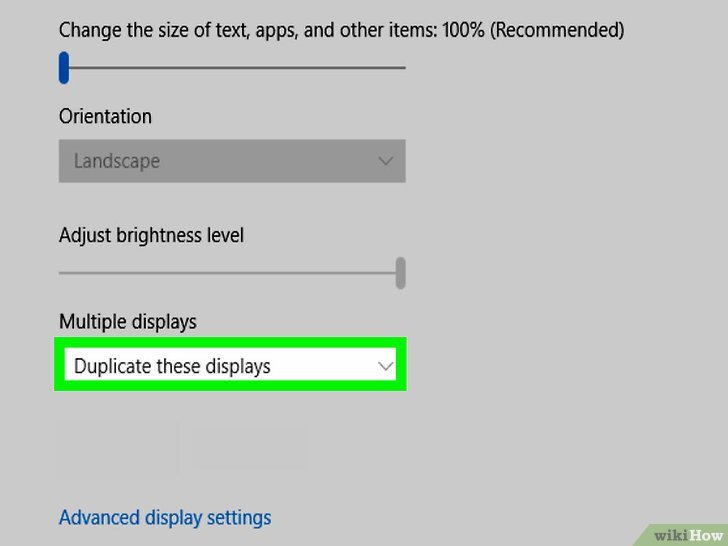
- Configure Display Settings: Once both monitors are connected, open your computer’s display settings. This process typically involves right-clicking on the desktop and selecting “Display settings.” The specific method may vary depending on the operating system.
- Arrange Displays: Use the display settings to arrange the monitors side-by-side, or in other configurations that meet your needs.
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
Occasionally, connection issues may arise. Troubleshooting these issues can be done systematically.
- No Signal: If no signal is displayed on either monitor, check the following: Ensure that the cables are securely plugged into both the computer and the monitor. Verify that the monitors are powered on. Try using different cables or ports if possible. Check your computer’s display settings for any configuration errors. Restarting both the computer and the monitors can sometimes resolve the issue.
Compatibility Table
The following table summarizes the compatibility of different ports.
| Device Port | Monitor Port Compatibility |
|---|---|
| Laptop HDMI | HDMI, DisplayPort (via adapter) |
| Desktop Graphics Card DisplayPort | DisplayPort, HDMI (via adapter) |
Configuring the Display Settings

Once your monitors are physically connected, configuring their display settings within your operating system is crucial for optimal performance and a seamless user experience. Proper configuration allows for adjustments in resolution, refresh rate, and monitor arrangement, enhancing productivity and visual clarity. This process ensures that your monitors function harmoniously, displaying content correctly and efficiently.
Adjusting Screen Resolution and Refresh Rate
Proper resolution and refresh rate settings are essential for a clear and smooth visual experience. Incorrect settings can lead to blurry images, flickering, or screen tearing. Choosing the appropriate resolution balances image quality with the capabilities of your display and graphics card. The refresh rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), determines how many times per second the image on the screen is updated.
A higher refresh rate generally results in smoother motion, particularly beneficial for fast-paced activities like gaming.
Arranging the Monitors
The arrangement of your monitors significantly impacts your workflow. Optimizing the layout allows for efficient multitasking and minimizes visual fatigue. Common arrangements include side-by-side configurations, where each monitor displays a different application, or vertically stacked layouts, which can be useful for displaying long documents or multiple windows simultaneously. Experiment with different configurations to find the layout that best suits your needs.
Setting Up Multiple Workspaces or Virtual Desktops
Multiple workspaces or virtual desktops offer a way to organize your applications and tasks on your dual monitor setup. This feature allows you to group related tasks or applications on separate virtual desktops, making it easier to switch between different sets of windows and applications. Virtual desktops can be particularly useful for managing numerous open programs or projects without cluttering one screen.
Changing Screen Resolution in Windows
This table Artikels the steps to adjust the screen resolution in Windows. This procedure is crucial for optimizing the visual experience and ensuring compatibility between your monitors and your operating system.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Open Display Settings. This can typically be accessed through the Start Menu or the Control Panel. |
| 2 | Select “Resolution” from the available options within the Display Settings. |
| 3 | Choose a suitable resolution from the dropdown list. Consider the resolution supported by your monitors and graphics card. A higher resolution typically provides more detail, but may require more processing power. |
| 4 | Click “Apply” to implement the chosen resolution. Your system may prompt you to restart for the changes to take effect. |
Advanced Dual Monitor Techniques
Expanding beyond basic setup, mastering advanced dual monitor techniques unlocks enhanced productivity and personalized experiences. These techniques go beyond simply connecting and configuring displays, delving into optimizing performance, tailoring setups for specific tasks, and fine-tuning visual settings for optimal viewing.Leveraging display extenders or splitters, fine-tuning display settings for peak performance, and tailoring the setup for specific applications, like gaming or video editing, are crucial steps.
Understanding these advanced methods allows for a smoother, more efficient, and visually appealing dual monitor setup.
Display Extenders and Splitters
Display extenders and splitters offer diverse functionalities for managing dual monitors. Display extenders create a single, larger workspace by expanding the existing desktop across both screens. Splitters, on the other hand, typically connect multiple devices to a single display output. This allows a variety of devices to use a single monitor, though performance may vary.
- Extenders allow you to use both monitors as one large screen, ideal for tasks requiring a wide workspace, such as document editing or spreadsheet work. A single application can utilize the combined space, enhancing efficiency.
- Splitters, in contrast, may be less effective for extending the desktop, and instead focus on connecting different sources (such as laptops or other devices) to a single display output, facilitating seamless multi-device use.
Optimizing Dual Monitor Performance
Proper configuration is key to achieving optimal performance with dual monitors. Multiple factors influence performance, from graphics card capabilities to monitor resolutions. Modern graphics cards are designed to manage multiple displays efficiently, and understanding how to utilize their capabilities is critical for performance optimization.
- Ensure your graphics card supports the resolution and refresh rate of both monitors. Check the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure compatibility.
- Update your graphics drivers to the latest versions. These updates often include performance improvements and support for new displays.
- Monitor settings can affect performance. Adjust refresh rates and resolutions to match the capabilities of your system and the specific demands of your tasks. For example, if you are primarily using your monitors for web browsing and document editing, lower resolutions and refresh rates may be sufficient. However, for gaming or video editing, higher resolutions and refresh rates are often necessary.
Dual Monitors for Gaming
Gaming with dual monitors can dramatically enhance the gaming experience. Utilizing two screens for in-game visuals and overlay information can provide a more immersive and strategic advantage. Careful setup is key to ensuring a smooth and responsive gaming environment.
- Configuring one screen for the game’s main display and another for overlay information, such as chat or minimaps, significantly enhances the gaming experience. This approach creates a more immersive and strategically sound gameplay.
- Adjusting display settings, including refresh rate and resolution, is crucial for optimal performance. Higher refresh rates and resolutions contribute to smoother gameplay, but may require more processing power.
- Ensure your graphics card is powerful enough to support the desired resolution and refresh rate on both monitors. This will prevent performance bottlenecks during gameplay.
Dual Monitors for Specific Applications
Different applications benefit from dual monitors in unique ways. Video editing, graphic design, and multitasking are just a few examples.
- Video Editing: Dual monitors allow video editors to simultaneously view the source footage and the edited output, enabling faster and more efficient editing workflows.
- Graphic Design: Graphic designers can utilize dual monitors for viewing different design elements and palettes alongside the main design canvas, increasing efficiency and accuracy.
- Multitasking: For users who frequently switch between multiple applications, dual monitors can greatly enhance productivity by enabling the simultaneous display of multiple windows.
Adjusting Monitor Settings for Color Accuracy
Color accuracy is crucial for tasks requiring precise color representation, such as photography, graphic design, and video editing. Proper calibration ensures accurate color reproduction across different applications.
- Calibration Tools: Utilize dedicated color calibration tools or software to adjust monitor settings for optimal color accuracy. These tools provide specific instructions to achieve accurate color reproduction.
- Color Profiles: Applying appropriate color profiles for your specific tasks can significantly improve color accuracy. Matching the profile to the intended use ensures a consistent color representation across different applications.
- Monitor Settings: Adjusting monitor settings such as gamma, color temperature, and brightness can further refine color accuracy. Experiment with these settings to find the optimal balance for your specific needs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Setting up dual monitors can sometimes present unexpected challenges. This section delves into common problems encountered during dual monitor setup and provides practical solutions to overcome them. Understanding these issues and their resolutions will ensure a smooth and stable dual monitor experience.Troubleshooting dual monitor setups requires a systematic approach. Identifying the source of the problem is crucial before implementing a solution.
This often involves checking hardware connections, adjusting display settings, and updating drivers. By following the detailed steps Artikeld below, you can effectively diagnose and resolve various dual monitor issues.
Identifying Flickering and Screen Tearing
Flickering and screen tearing are common issues that can disrupt the smooth display of dual monitors. Flickering often indicates a problem with the monitor’s power supply, connection, or the graphics card. Screen tearing, characterized by jagged or distorted lines, typically stems from a mismatch between the monitor’s refresh rate and the graphics card’s output.
- Flickering can be resolved by checking the power supply for the monitors, ensuring secure connections, and verifying the cable type for compatibility. If issues persist, consider updating the graphics card drivers.
- Screen tearing can be addressed by adjusting the refresh rates of the monitors. If the refresh rates are different, try synchronizing them to a common value. Additionally, updating graphics drivers or using tearing-reducing technologies in the display settings can help resolve this issue.
Diagnosing and Resolving Graphics Card Driver Issues
Graphics card drivers are essential for optimal dual monitor performance. Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to various display problems, including flickering, screen tearing, and distorted images. Regularly updating drivers is a proactive step in maintaining a stable dual monitor setup.
- Driver Updates: Downloading and installing the latest graphics card drivers from the manufacturer’s website is crucial. Ensure the drivers are compatible with your operating system and graphics card model. Follow the installation instructions carefully.
- Driver Conflicts: Ensure the graphics card drivers are compatible with your operating system and monitor settings. Sometimes, conflicting drivers or outdated versions can cause instability.
Resolving Monitor Compatibility Issues
Monitor compatibility issues can manifest as display errors or connection problems. This section Artikels methods for diagnosing and resolving incompatibility issues between your monitors and graphics card.
- Monitor Specifications: Carefully review the specifications of your monitors, including resolution, refresh rate, and connection type. Ensure these specifications align with your graphics card’s capabilities. Mismatches can lead to display problems.
- Resolution and Refresh Rate: Adjusting the resolution and refresh rate settings of the monitors to match the graphics card’s capabilities can resolve compatibility issues. Use the recommended settings to avoid conflicts. For example, using 1920×1080 for a monitor with a 60Hz refresh rate will generally work better than using 2560×1440 with a 144Hz refresh rate.
Troubleshooting Connection Problems
Connection problems are common during dual monitor setups. This section provides a troubleshooting guide to help resolve issues related to the connections between the monitors and the graphics card.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No signal to one or both monitors | Loose or damaged cable, incorrect connection type, graphics card malfunction. | Check cable connections, ensure the correct cable type is used (e.g., DisplayPort, HDMI), and consider checking the graphics card. Try another cable or port if possible. |
| Monitor displays blank | Incorrect cable, damaged cable, monitor malfunction, graphics card malfunction, or display setting issue. | Check the cable connections, try another cable or port, and verify the monitor’s power supply. Check the display settings and ensure the monitors are correctly detected by the system. |
| Distorted image | Incorrect cable, damaged cable, or resolution mismatch between the monitor and graphics card. | Check cable connections, try another cable or port, and ensure the resolution settings are appropriate for the monitor and graphics card. |
Last Word

In conclusion, setting up a dual monitor display is a straightforward process when approached methodically. This guide has provided a detailed roadmap, from initial hardware selection to advanced configuration techniques, ensuring a smooth and productive transition to a dual-monitor environment. Remember to consider your specific needs and preferences when choosing monitors and configuring the setup. With a little patience and attention to detail, you’ll be well on your way to experiencing the enhanced productivity and visual clarity a dual monitor setup offers.