Choosing the right motherboard for your CPU is crucial for optimal system performance and stability. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the factors to consider when ensuring compatibility, from understanding socket types and chipset specifications to checking CPU requirements and troubleshooting potential issues. Proper matching ensures a smooth and efficient computing experience.
This detailed exploration of motherboard and CPU compatibility will cover essential aspects, including the identification of crucial specifications, the matching process, and advanced considerations like memory and power supply requirements. A deep dive into troubleshooting common compatibility problems will also be presented, providing a practical and problem-solving approach.
Understanding CPU Compatibility
Selecting a motherboard that is compatible with your CPU is crucial for a stable and high-performing system. A mismatch can lead to system instability, boot failures, and even hardware damage. This section delves into the key factors that determine compatibility, ensuring you make the right choice for your needs.CPU and motherboard compatibility hinges on several interconnected factors, primarily the socket type, chipset, and CPU specifications.
Understanding these factors is paramount to avoiding costly mistakes and ensuring a smooth, efficient computing experience.
CPU Socket Type
The socket type is a critical aspect of CPU compatibility. It physically defines the connection point between the CPU and the motherboard. A mismatch in socket type will prevent the CPU from being installed, rendering the selection process futile.
- The socket type, often denoted by abbreviations like LGA (Land Grid Array) or PGA (Pin Grid Array), dictates the physical form factor of the CPU. This determines the number of pins and their arrangement, which must precisely align with the motherboard socket for proper functionality. This alignment is essential for a successful connection and prevents damage to either component.
- Different socket types are designed for different CPU architectures and generations. A CPU intended for one socket type will not fit in a socket designed for another, regardless of the CPU’s overall specifications. This is a fundamental aspect of compatibility and a crucial factor in the selection process.
- For example, an LGA 1700 socket motherboard will only accept CPUs designed for that socket type, such as Intel Core processors in the 13th generation. Attempting to install a CPU designed for an LGA 1151 socket into an LGA 1700 socket will result in a non-functional system.
Chipset Compatibility
The motherboard’s chipset plays a crucial role in determining the CPU’s performance and functionalities. It acts as a bridge between the CPU and other hardware components.
- The chipset’s capabilities directly impact the CPU’s ability to interact with memory, storage devices, and other peripherals. The chipset’s specifications and features must align with the CPU’s requirements for optimal performance.
- Choosing a motherboard with a chipset not compatible with the CPU will likely limit the CPU’s performance. For example, if the chipset doesn’t support the CPU’s memory controller, the system may not be able to utilize high-speed memory modules.
CPU Socket Type Comparison
The table below provides a comparison of different CPU socket types, highlighting their pin configurations and corresponding motherboard support. Note that this is not an exhaustive list, and new socket types are continually introduced.
| Socket Type | Pin Configuration | Typical CPU Compatibility | Motherboard Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| LGA 1700 | 1700 pins | Intel 13th Gen Core CPUs | Motherboards designed for LGA 1700 |
| LGA 1200 | 1200 pins | Intel 11th and 12th Gen Core CPUs | Motherboards designed for LGA 1200 |
| AM4 | 1331 pins | AMD Ryzen 3000 and 5000 series CPUs | Motherboards designed for AM4 |
| AM3+ | 940 pins | AMD Phenom II and older CPUs | Motherboards designed for AM3+ |
Implications of Incompatible Components
Incompatibility between the CPU and motherboard can lead to various negative consequences, affecting system stability and performance.
- A mismatched CPU and motherboard combination can result in system instability, including boot failures, frequent crashes, and unpredictable behavior. This can range from simple error messages to complete system failure.
- Furthermore, performance issues can arise from an incompatible configuration. The system may not be able to utilize the CPU’s full potential, leading to slowdowns in tasks requiring significant processing power.
- In extreme cases, incompatible components may cause physical damage to either the CPU or motherboard. This damage is often irreversible, requiring replacement of the affected component.
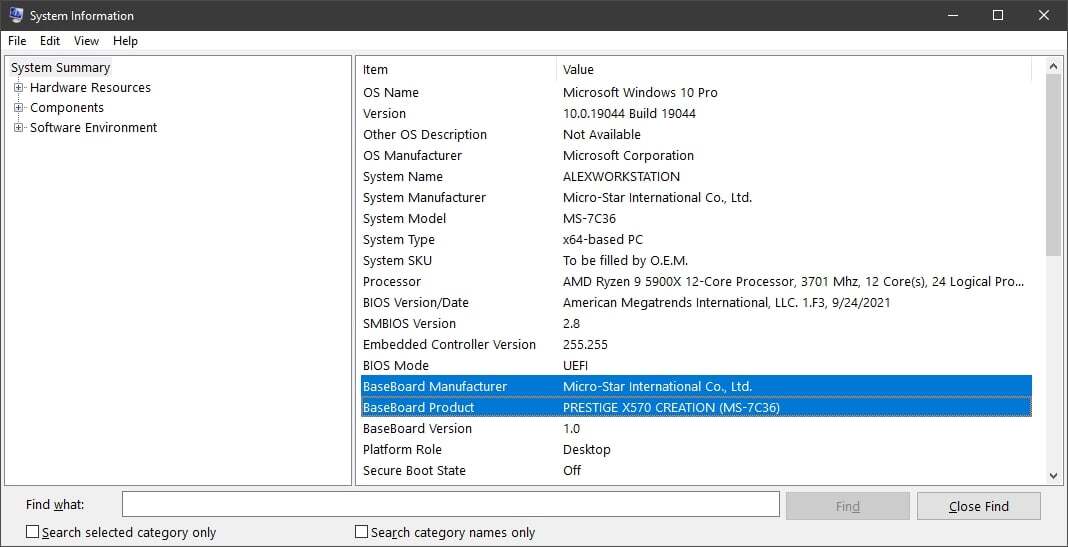
Identifying Motherboard Specifications
Carefully examining motherboard specifications is crucial for ensuring CPU compatibility. This process involves understanding the key features and components that determine if a processor will function correctly with a given motherboard. A mismatch can lead to significant issues, ranging from a failure to boot to instability during operation. Thorough investigation of these specifications is vital for successful system building.Precise identification of motherboard specifications allows for the selection of a compatible motherboard for a specific CPU.
The motherboard acts as the central hub, connecting all components of the computer system. Therefore, compatibility between the CPU and the motherboard is paramount for optimal performance. Understanding the specifics of each component ensures that the system operates smoothly and reliably.
Chipset
The chipset is a crucial component that dictates which CPUs a motherboard can support. It acts as a bridge between the CPU and other hardware components, influencing compatibility. Different chipsets support different CPU socket types and instruction sets. A motherboard with an incompatible chipset will prevent a CPU from functioning properly. Manufacturers often publish detailed specifications outlining the supported CPUs for each chipset.
CPU Socket Type
The CPU socket type is a critical factor in CPU compatibility. It defines the physical form factor and pin configuration of the CPU socket on the motherboard. Each CPU socket type is unique, and CPUs designed for a specific socket will not fit into a different socket type. A motherboard designed for an LGA 1700 socket, for instance, will not accommodate an AM4-based CPU.
Checking the CPU socket type is essential to ensure compatibility before purchase.
Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits, or ICs, on the motherboard play a role in CPU compatibility. These circuits are responsible for various functionalities, including data transfer, power management, and communication protocols. Some integrated circuits are designed to work seamlessly with certain CPU architectures. Incompatibilities between integrated circuits and CPU architectures can lead to system instability or non-functionality. It is important to examine the integrated circuits in relation to the CPU architecture to avoid potential issues.
Key Motherboard Specifications for CPU Compatibility
| Specification | Importance for CPU Compatibility |
|---|---|
| Chipset | Determines supported CPU socket types, instruction sets, and overall compatibility. |
| CPU Socket Type | Must match the CPU’s socket type for physical and electrical compatibility. |
| Integrated Circuits (e.g., Southbridge, Northbridge) | Impacts data transfer, power management, and communication protocols that are critical to CPU interaction. |
| Memory Slots | Critical for CPU compatibility if the CPU requires specific memory standards. |
| PCIe Slots | Affects compatibility if the CPU relies on specific PCIe standards. |
Finding Motherboard Specifications
Manufacturers provide comprehensive documentation outlining the specifications of their motherboards. These documents typically include detailed information about supported CPU socket types, chipsets, and integrated circuits. Consult the motherboard’s manufacturer website or user manual for accurate and detailed information about the supported CPU models. A clear understanding of these details is crucial for ensuring proper system functionality.
Checking CPU Specifications

Carefully examining CPU specifications is critical for ensuring motherboard compatibility. A mismatch between CPU and motherboard can lead to various problems, ranging from the inability to boot to complete system instability. Understanding the crucial elements of a CPU’s specifications is essential for a successful and reliable computer setup.Accurate identification of a CPU’s specifications is fundamental for selecting the correct motherboard.
This process involves reviewing key attributes such as socket type, architecture, and features. Matching these attributes with the motherboard’s capabilities guarantees a seamless integration and optimal system performance.
CPU Socket Type and Compatibility
The CPU socket type is a crucial factor in motherboard compatibility. A motherboard is designed with a specific socket type, and only CPUs compatible with that socket can be installed. Mismatched socket types will prevent the CPU from fitting into the motherboard. The socket type dictates the physical form factor and electrical connections required for proper communication between the CPU and motherboard.
CPU Architecture and Motherboard Selection
CPU architecture significantly impacts motherboard selection. Different architectures require different sets of instructions and capabilities from the motherboard. For example, a newer architecture might require more advanced features like PCIe 4.0 or 5.0 slots for optimal performance. Compatibility issues arise when a motherboard does not support the CPU’s architecture or its features.
CPU Features and Motherboard Choice
Certain CPU features significantly influence motherboard selection. Integrated graphics, for example, might necessitate a motherboard with appropriate video output options. Memory support is another crucial aspect; a motherboard must support the specific memory types and speeds compatible with the CPU. If the motherboard does not support the features present on the CPU, it will affect the performance of the CPU.
Crucial CPU Specifications for Compatibility
- Socket Type: This is the physical connector on the motherboard where the CPU sits. A mismatch here is a common cause of incompatibility. For instance, an AM4 socket CPU will not fit into a LGA1700 socket motherboard.
- CPU Architecture: The instruction set and design principles of the CPU. This influences features like memory controllers and integrated graphics capabilities.
- Integrated Graphics: If the CPU has integrated graphics, the motherboard needs compatible video output options (e.g., DisplayPort, HDMI). Not having these connections will lead to problems.
- Memory Support: The CPU’s memory controller determines the supported memory types (DDR3, DDR4, DDR5) and speeds. A motherboard must support these memory specifications for proper operation.
- PCIe Support: Modern CPUs support different generations of PCI Express (PCIe) for connecting expansion cards. The motherboard needs to support the same or a higher generation of PCIe for optimal performance.
Comparison Table of CPU Models, Socket Types, and Compatible Motherboards
| CPU Model | Socket Type | Compatible Motherboards |
|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i5-13600K | LGA1700 | Motherboards with LGA1700 socket and supporting the i5-13600K’s features. |
| AMD Ryzen 7 7700X | AM5 | Motherboards with AM5 socket and supporting the Ryzen 7 7700X’s features. |
| Intel Core i7-12700 | LGA1700 | Motherboards with LGA1700 socket and supporting the i7-12700’s features. |
Note: This table provides a simplified example. The specific compatibility information should always be confirmed on the manufacturer’s websites.
Matching CPU and Motherboard
Selecting a compatible motherboard for your CPU is crucial for optimal system performance and stability. Proper matching ensures the CPU and motherboard are designed to work seamlessly together, leveraging the full potential of both components. This section details the vital considerations for achieving this compatibility.
CPU and Motherboard Compatibility Factors
Compatibility hinges on several key factors. These include the CPU socket type, chipset support, and the motherboard’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) version. The socket type, a physical connector on the motherboard, must precisely match the CPU’s physical form factor. The chipset, the motherboard’s integrated circuit, dictates the supported CPU generations and features. The BIOS is crucial; it must be updated to recognize and support the new CPU, sometimes requiring a BIOS update.
Matching CPU and Motherboard by Socket Type
A fundamental step involves verifying that the CPU and motherboard share the same socket type. Different CPU architectures require different socket types, and attempting to install a CPU into an incompatible socket will result in damage to the CPU and/or motherboard. For instance, an AMD AM4 socket CPU cannot be installed into an Intel LGA1700 socket motherboard.
Ensuring Motherboard Supports CPU Features
Motherboard chipsets are designed to support specific CPU features. Features like integrated graphics, PCIe lanes, and memory support all require corresponding support from the motherboard. A motherboard that lacks the necessary support for the CPU’s features will limit the system’s overall functionality. For example, a CPU with a high-speed integrated graphics core will not perform as expected if the motherboard chipset does not adequately support its features.
Performance Considerations in CPU-Motherboard Pairing
Choosing a motherboard based on the CPU’s performance requirements is essential. The motherboard’s chipset and its associated features will determine the overall performance and capabilities of the system. Factors like memory support, PCIe slots, and onboard controllers will significantly influence the system’s performance. A higher-end CPU will require a motherboard that can handle its demanding performance demands.
Suggested CPU and Motherboard Pairings
| Performance Level | Suggested CPU | Suggested Motherboard | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | Intel Core i3-12100 | ASUS PRIME B660M-A | Provides basic functionality and budget-friendly options. |
| Mid-Range | AMD Ryzen 5 7600X | ASUS ROG STRIX B650-A GAMING | Offers a balance of performance and features. |
| High-End | Intel Core i9-13900K | ASUS ROG Maximus Z790 HERO | Supports high-end CPU features and demanding applications. |
Troubleshooting CPU-Motherboard Incompatibility
Incompatibility issues can arise from various sources. One potential issue is a mismatch in socket types, resulting in physical incompatibility. Another is a BIOS that does not support the CPU, leading to boot failures or system instability. A lack of compatibility between the CPU and the motherboard’s chipset can also prevent the CPU from functioning correctly.
- Socket Mismatch: Verify the socket types of both components are identical. Incorrect socket types will lead to physical damage. A replacement motherboard with the correct socket is required in this case.
- BIOS Issues: Ensure the motherboard’s BIOS is updated to the latest version compatible with the CPU. BIOS updates often resolve compatibility issues by improving the CPU’s recognition by the motherboard.
- Chipset Limitations: Check the motherboard’s chipset documentation to confirm compatibility with the CPU’s features. If the chipset doesn’t support the CPU’s features, a motherboard upgrade is necessary.
- Component Damage: Inspect both components for any visible damage. Faulty components must be replaced to resolve the incompatibility.
Advanced Considerations
Selecting a compatible motherboard for your CPU involves more than just checking for compatibility lists. Several advanced factors significantly influence performance and stability. Understanding these intricacies ensures a smooth and efficient system.
Memory Compatibility
Memory compatibility plays a crucial role in system performance. Different motherboards support specific types and capacities of RAM modules. Mismatched memory can lead to boot failures, instability, or even system crashes. Proper selection of RAM modules is vital for optimal system performance.
Identifying Compatible Memory Modules
To identify compatible memory modules, consult the motherboard’s specifications. These specifications typically Artikel the supported memory types (e.g., DDR4, DDR5), frequencies (e.g., 3200 MHz, 3600 MHz), and maximum capacity. Furthermore, the motherboard manual often provides a comprehensive list of compatible memory modules. Matching the memory specifications with the motherboard is essential for avoiding compatibility issues.
Power Supply Requirements
The power supply (PSU) is a critical component in the CPU-motherboard selection process. The CPU and motherboard, along with other components, have specific power consumption needs. A PSU with insufficient wattage can lead to instability, slowdowns, and potential damage to components. Careful consideration of the total power consumption of all components is vital when choosing a PSU.
For example, a high-end CPU and a high-end graphics card will demand a more powerful PSU than a basic system. Consult the motherboard and CPU specifications to determine the total power requirements.
BIOS Settings
BIOS settings are crucial for configuring and optimizing the CPU-motherboard interaction. The BIOS allows you to fine-tune settings, including CPU frequency, voltage, and memory timings. These adjustments can significantly impact performance and stability. Proper BIOS settings ensure optimal performance and stability, enabling the system to function as intended.
Ensuring Motherboard Features Meet Your Needs
Beyond basic compatibility, consider the motherboard’s features. Look for features like the number of expansion slots (PCIe), the presence of specific ports (USB, SATA, etc.), and integrated graphics capabilities. These features should align with your needs for expansion and connectivity. For example, if you need multiple graphics cards, a motherboard with multiple PCIe slots is crucial. Similarly, if you require a high number of storage drives, ensure the motherboard has sufficient SATA ports.
Resources for Further Research
Numerous resources can assist in your research. Manufacturer websites often provide detailed specifications and compatibility guides. Online forums dedicated to PC hardware offer valuable insights and discussions from experienced users.
Troubleshooting Compatibility Issues
![Find a CPU that is Compatible with Your Motherboard [2025] Find a CPU that is Compatible with Your Motherboard [2025]](https://wayzen.web.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/cpu-compatiblity-fun-art-1-768x432-1.png)
Ensuring your CPU and motherboard work seamlessly together is crucial for optimal system performance. This section details the steps to diagnose and resolve compatibility problems, guiding you through identifying the source of the issue and implementing effective solutions.A well-defined troubleshooting process allows you to pinpoint the root cause of compatibility problems, whether it stems from incorrect component selection or unforeseen hardware conflicts.
Following a systematic approach to resolving these issues ensures a smooth installation and prevents frustration.
Diagnosing CPU-Motherboard Compatibility Problems
Proper diagnosis is the first step in resolving compatibility issues. This involves systematically checking for common problems and identifying the source of the incompatibility. Careful observation and methodical testing can help isolate the problem, whether it’s a configuration error or a faulty component.
Identifying the Source of Incompatibility Issues
Identifying the source of incompatibility issues involves a combination of methodical checking and systematic testing. This process begins by verifying that all components meet the minimum requirements of the motherboard. Further steps may include checking for BIOS updates, examining CPU and motherboard documentation, or even verifying power supply compatibility.
Common Incompatibility Problems and Their Solutions
Various issues can lead to incompatibility problems between a CPU and motherboard. These include incorrect CPU socket type, incompatible CPU voltage requirements, or issues with the motherboard’s BIOS settings. Properly understanding these common problems is key to resolving them.
- Incorrect CPU Socket Type: Mismatching the CPU socket type with the motherboard socket is a frequent cause of incompatibility. The CPU must physically fit into the motherboard’s socket. Double-checking the socket type listed in the motherboard’s documentation and the CPU packaging is essential. If the CPU socket type is incorrect, the CPU will not be compatible with the motherboard.
- Incompatible CPU Voltage Requirements: The CPU requires specific voltage levels for proper operation. If the motherboard cannot supply the required voltage or if the CPU draws excessive power, it can lead to incompatibility. Reviewing the CPU’s specifications and the motherboard’s specifications is crucial. Ensure the motherboard’s voltage regulator can support the CPU’s voltage needs.
- Issues with Motherboard’s BIOS Settings: Incorrect BIOS settings can also cause compatibility problems. A misconfigured BIOS setting for CPU parameters can lead to incompatibility. Carefully reviewing and adjusting BIOS settings according to the CPU’s specifications is important.
Troubleshooting Techniques for CPU-Motherboard Conflicts
Troubleshooting techniques for CPU-motherboard conflicts often involve a methodical approach to identify the root cause. These techniques encompass reviewing system documentation, examining physical connections, and considering software updates.
- Review System Documentation: Thoroughly reviewing the documentation for both the CPU and the motherboard is critical. This step includes understanding the compatibility charts, supported CPU models, and BIOS settings. Misinterpreting these documents can result in compatibility issues.
- Examine Physical Connections: Ensure all connections, including the CPU and RAM, are securely installed. Loose or incorrect connections can cause intermittent issues or total system failure. Checking the CPU and RAM is vital.
- Consider Software Updates: Software updates, including BIOS updates, can resolve compatibility issues. Outdated BIOS versions may not support newer CPU models. Checking for the latest BIOS updates for the motherboard is a crucial step.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide for Resolving Incompatibility Issues
A step-by-step guide for resolving incompatibility issues helps ensure a methodical approach to problem-solving. This involves systematically checking each step to identify the source of the incompatibility.
- Verify CPU and Motherboard Compatibility: Consult the motherboard’s documentation and the CPU’s specifications to confirm compatibility.
- Check Physical Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and properly installed. Verify that the CPU is correctly seated in the socket.
- Review BIOS Settings: Verify BIOS settings for CPU parameters and ensure they align with the CPU’s specifications.
- Update BIOS: If possible, update the motherboard’s BIOS to the latest version.
- Test with Different Components: If the problem persists, try installing the CPU on a different motherboard (if available) or using a different CPU on the same motherboard.
Summary of Common Compatibility Problems and Solutions
The following table summarizes common compatibility problems and their solutions, providing a quick reference guide for resolving issues.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incorrect CPU Socket Type | Ensure the CPU fits the motherboard’s socket type. |
| Incompatible CPU Voltage Requirements | Verify the motherboard can provide the required voltage levels. |
| Issues with Motherboard’s BIOS Settings | Review and adjust BIOS settings according to the CPU’s specifications. |
| Loose Connections | Ensure all connections are secure. |
| Outdated BIOS | Update the motherboard’s BIOS to the latest version. |
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, selecting a compatible motherboard for your CPU involves a careful consideration of various specifications and requirements. By understanding the intricacies of socket types, chipsets, and CPU features, you can ensure a seamless and high-performing system. This guide has provided a comprehensive framework for navigating this process, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and avoid potential compatibility issues.
Ultimately, selecting the correct components ensures a smooth and enjoyable computing experience.