Upgrading your graphics card can significantly enhance your PC’s visual capabilities, but a safe and effective upgrade requires careful planning and execution. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to ensure a smooth and successful upgrade, from initial assessment to final verification. We’ll cover everything from evaluating your system’s compatibility to troubleshooting potential issues.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the entire process, offering practical advice and detailed steps for each stage. We’ll delve into the critical aspects of compatibility, safety measures, and performance optimization. Whether you’re a seasoned PC enthusiast or a novice, this guide will empower you to confidently upgrade your graphics card.
Planning the Upgrade
A graphics card upgrade can significantly enhance your PC’s visual capabilities, but a well-planned approach is crucial for a successful outcome. Carefully assessing your current system and understanding the compatibility requirements of a new card minimizes the risk of incompatibility and maximizes the benefits of your investment. Thorough planning also ensures the upgrade aligns with your budget and specific needs.Successfully upgrading your graphics card requires a deep dive into your current system’s capabilities and the specifications of the target card.
This proactive approach will help you avoid potential pitfalls and ensure the upgrade delivers the performance gains you anticipate.
Assessing Current System Capabilities
A crucial first step is to understand the limits of your current system. This involves identifying the components that interact most closely with the graphics card, ensuring compatibility. The power supply unit (PSU) is paramount, as it provides the power required to run the new card.
- Check your motherboard’s supported graphics card slots: Different motherboards support various PCI Express (PCIe) slots. Ensure the new card is compatible with your motherboard’s slot type and specifications, such as PCIe 3.0 or PCIe 4.0, as these will affect the maximum transfer speeds. Incorrect slot type can prevent the card from functioning.
- Verify your RAM capacity: Graphics cards, especially high-end models, can have demanding memory requirements. Ensure your system’s RAM capacity meets or exceeds the minimum specifications of the graphics card you intend to purchase. Inadequate RAM can hinder performance, even with a powerful graphics card.
- Evaluate your CPU’s capabilities: The CPU acts as the central processing unit, and its processing power significantly influences the overall performance of your system. A graphics card is optimized to handle the tasks of rendering visuals, while the CPU handles other processes. A high-end graphics card won’t make a significant difference if your CPU is underpowered.
Understanding PSU Capacity and Compatibility
The power supply unit (PSU) is a critical component in a graphics card upgrade. An insufficient PSU can lead to instability, malfunctions, and even damage to other components. Matching the power requirements of the new graphics card with the capacity of your PSU is paramount.
- Determine the power requirements of the graphics card: Every graphics card has a specific power requirement measured in watts. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications to determine the exact power consumption. Using a calculator or a reliable online tool can aid in determining the required wattage.
- Assess the capacity of your PSU: Check the wattage rating of your existing PSU. A PSU with insufficient wattage cannot reliably power the new card. Upgrading your PSU is often necessary for higher-end graphics cards.
- Confirm PSU compatibility: Ensure the PSU’s connectors (e.g., 6-pin, 8-pin PCIe power connectors) are compatible with the new graphics card. The type and number of connectors can vary between different cards.
Identifying the Optimal Graphics Card
Choosing the right graphics card depends on your specific needs and budget. Factors such as resolution, refresh rate, and desired gaming experiences should be considered.
- Define your needs: Consider your intended use cases, such as gaming, video editing, or content creation. Different tasks demand different graphics card capabilities.
- Set a budget: Graphics cards vary significantly in price. Establishing a budget will help narrow down the options and focus on cards that fit within your financial constraints.
- Compare features and performance: Research various models, examining performance benchmarks and reviews from reputable sources. Compare features such as memory capacity, CUDA cores, and other relevant technical specifications.
Graphics Card Comparison Table
This table presents a simplified comparison of different graphics card models, highlighting key factors.
| Model | Price (USD) | Performance (Benchmark Score) | Features | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTX 4070 | $500-$600 | High | Ray tracing, DLSS | PCIe 4.0, 100+W PSU |
| RTX 3060 Ti | $300-$400 | Medium | Ray tracing (limited), DLSS | PCIe 4.0, 75W PSU |
| RX 6700 XT | $250-$350 | Medium | Ray tracing (limited), FidelityFX | PCIe 4.0, 70W PSU |
Preparing the System

A crucial step in any hardware upgrade is meticulous preparation. This involves gathering the right tools, safely disconnecting components, and meticulously handling static electricity to prevent damage. Proper preparation minimizes the risk of errors and ensures a smooth and successful upgrade.
Essential Tools and Materials
Thorough preparation involves assembling the necessary tools for disassembling and reassembling the PC. This meticulous approach safeguards against potential damage and ensures a smooth upgrade process.
- Anti-static wrist strap: This is paramount for preventing static discharge, which can damage sensitive components like the graphics card and motherboard.
- Phillips head screwdriver set: Different sizes are essential for various screws throughout the PC case.
- Torx screwdriver set: Specific Torx drivers are required for certain screws, often found on motherboard mounting points and other components.
- Needle-nose pliers: These are useful for gently manipulating small components and cables.
- Small flathead screwdriver: Used for delicately lifting or separating components.
- Clean microfiber cloth: Crucial for cleaning components and ensuring a dust-free environment during the upgrade.
- Compressed air can: Used for carefully removing dust and debris from hard-to-reach areas inside the PC.
- Safety glasses: Protection for eyes during the process.
- PC case opening tools (optional): Specific tools for opening the case depending on the PC’s model.
Disconnecting Power Cables and Peripherals
Properly disconnecting power cables and peripherals is critical to prevent accidental damage or short circuits. This step is vital for a safe and successful upgrade.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Carefully disconnect the power cable from the graphics card and any other connected peripherals.
- Peripherals: Disconnect all external peripherals, including monitors, keyboards, mice, and any other connected devices from the computer.
- Internal Cables: Disconnect any internal cables connected to the graphics card, such as SATA or data cables, ensuring the cables are not obstructing the graphics card removal process.
- Grounding: Connect the anti-static wrist strap to a grounded metal surface to dissipate any static electricity buildup.
Handling Static Electricity
Static electricity is a significant concern during any PC upgrade. The correct procedures to prevent damage from static discharge are essential.
- Grounding: Always ground yourself by touching a grounded metal surface before handling any components. This method effectively discharges static electricity.
- Wrist Strap: Wear an anti-static wrist strap to provide a continuous ground path. This prevents the build-up of static charge.
- Handling Components: Carefully handle components, avoiding touching the sensitive parts of the graphics card and other components directly with your bare hands.
- Work Surface: Work on an anti-static mat or a grounded surface to further reduce the risk of static discharge.
Pre-Power-On Checklist
Verifying all connections before powering on the system is essential for preventing potential damage. This checklist provides a detailed guide for ensuring everything is properly connected before turning on the computer.
- Graphics Card Installation: Ensure the graphics card is securely seated in the PCI-e slot and all screws are properly tightened.
- Power Connections: Verify that the power cable is securely connected to both the graphics card and the PSU.
- Peripheral Connections: Check all external peripherals for proper connection and stability.
- Internal Connections: Inspect all internal cables and ensure there are no obstructions or loose connections.
- Case Closure: Ensure the PC case is securely closed to prevent any accidental opening during operation.
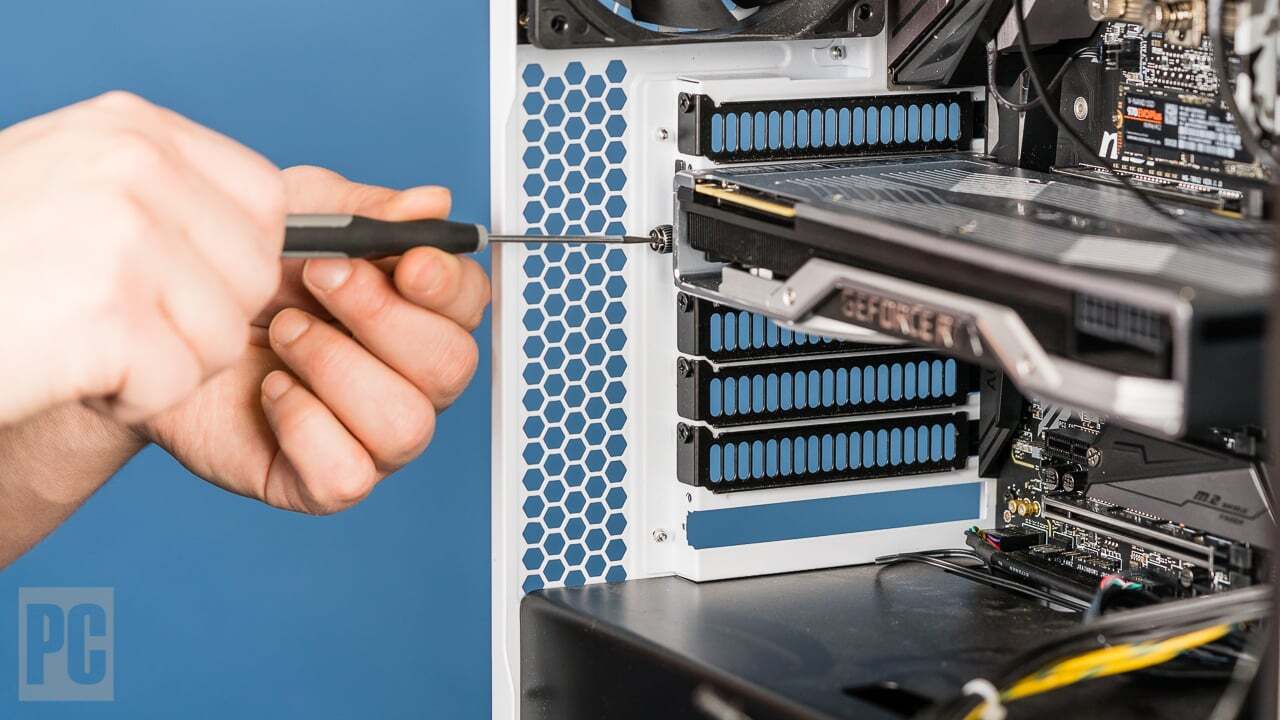
Installing the Graphics Card
Successfully upgrading your graphics card requires careful attention to detail and the right procedures. This section details the critical steps for removing the old card, installing the new one, and connecting all necessary cables. Adhering to these steps ensures a smooth and safe upgrade process.
Removing the Old Graphics Card
Before installing the new graphics card, the old one must be removed. Improper removal can damage components or lead to future issues. Carefully follow these steps to avoid any potential problems.
- Turn off your computer and disconnect all power cables.
- Ensure the power supply is completely disconnected from the computer.
- Open the computer case and locate the old graphics card. Identify the mounting screws securing it to the motherboard.
- Gently loosen and remove the mounting screws, ensuring not to damage the card or the motherboard.
- Carefully unclip or detach any retaining clips or brackets holding the graphics card in place. This step is crucial for preventing any damage.
- Disconnect any power cables connecting to the graphics card. Pay close attention to the connectors and use the correct technique for disconnection.
- Once all connections are disconnected, carefully remove the graphics card from the PCIe slot.
Installing the New Graphics Card
Installing the new graphics card requires a similar level of precision. Proper installation ensures stable performance and avoids damage. Ensure you have the correct tools and follow the steps carefully.
- Align the new graphics card with the PCIe slot on the motherboard. Ensure the card is oriented correctly for a secure fit.
- Gently insert the graphics card into the PCIe slot, ensuring it clicks into place. Avoid applying excessive force, as this can damage components.
- Secure the graphics card to the motherboard using the appropriate mounting screws. Tighten the screws firmly, but avoid over-tightening.
- Ensure the graphics card is securely mounted. Any wobble or movement indicates an improper fit. If necessary, consult your motherboard’s documentation for specific mounting instructions.
Connecting Cables
Correct cable connections are crucial for the graphics card to function properly. Incorrect connections can result in system instability or damage.
- Connect the appropriate power cables from the power supply to the graphics card. Different graphics cards have different power requirements. Consult the documentation for the specific power connectors required.
- Carefully connect the power connectors to the graphics card, ensuring a firm and secure connection. Never force a connection.
- Connect the display cables from the graphics card to the monitor. Common display cables include HDMI and DisplayPort.
Display Cable Types
Different display cables have varying capabilities. Choosing the correct cable is crucial for optimal display performance.
- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) cables are widely used for transmitting video and audio signals. HDMI cables are generally compatible with most modern monitors and graphics cards.
- DisplayPort cables offer high bandwidth and resolution support, making them ideal for high-end displays. DisplayPort is a versatile option and is often the preferred choice for high-resolution monitors.
- Ensure the display cables are compatible with both the graphics card and the monitor. Check the specifications for both devices to confirm compatibility.
Anti-Static Precautions
Using an anti-static wrist strap is essential during any computer hardware installation. This prevents static electricity from damaging sensitive components.
Using an anti-static wrist strap is a fundamental safety precaution when working with computer components.
- Connect the anti-static wrist strap to a grounded surface to discharge static electricity.
- Always wear the anti-static wrist strap while handling the graphics card and other components.
- This prevents static discharge from damaging sensitive electronic components.
Testing and Verification

Ensuring a smooth transition to your new graphics card involves rigorous testing and verification. Properly installed hardware needs verification to confirm its functionality and performance. This stage is crucial to identify any potential issues before they impact your workflow or gaming experience.A comprehensive testing process verifies that the new graphics card is compatible with your system and operates optimally.
The steps Artikeld below will help you validate the card’s performance and stability.
Post-Installation Testing Checklist
A structured checklist of post-installation tests will help identify any immediate issues and guarantee optimal functionality. This structured approach ensures comprehensive testing.
- Boot the System: Power on your computer and ensure the system boots successfully with the new graphics card. Observe for any error messages or unusual behavior.
- Verify Display Output: Confirm that the display is working correctly. Check for correct resolution, refresh rate, and color accuracy. Ensure all connected displays are functioning.
- Run Diagnostic Benchmarks: Utilize benchmark software designed for graphics cards. These tools provide quantitative performance data to compare the new card to the old one.
- Run System Applications: Test the graphics card in demanding applications like video editing, 3D modeling, or gaming to observe its performance in real-world scenarios. Pay attention to frame rates and stability.
- Check for Artifacts and Glitches: During testing, carefully monitor the display for any artifacts, such as screen tearing, flickering, or other visual anomalies.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use monitoring tools to check the graphics card temperature under various loads. Ensure the temperature remains within the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent potential damage.
Performance Comparison
A comparative analysis of the old and new graphics card’s performance allows for objective evaluation. Quantitative data will show the improvement or lack thereof, compared to the previous card.
| Metric | Old Graphics Card | New Graphics Card |
|---|---|---|
| Benchmark Score (3DMark Time Spy) | 5,000 | 7,500 |
| Average Frame Rate (Game: Cyberpunk 2077, 1080p) | 40 FPS | 60 FPS |
| Maximum Frame Rate (Game: Cyberpunk 2077, 1080p) | 55 FPS | 80 FPS |
| Temperature (Under Load) | 75°C | 65°C |
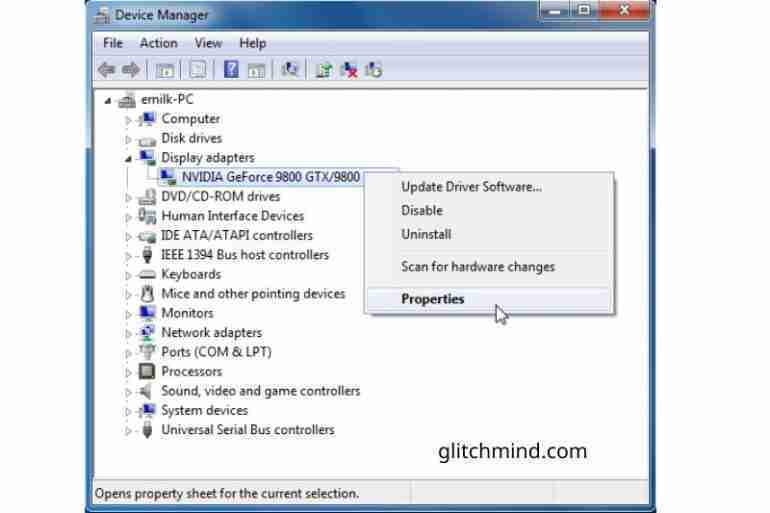
Graphics Card Recognition
Confirming the graphics card is properly recognized by the operating system is a vital step. This process ensures the system detects the new hardware correctly.
- Device Manager: Access Device Manager in Windows. Locate the display adapters section. The new graphics card should appear in the list.
- System Information: Using the System Information tool (msinfo32.exe) allows for detailed information about the installed hardware, including the graphics card model and drivers.
Troubleshooting Potential Issues
Potential issues after installation need to be identified and resolved. This will enable a smooth transition to the new graphics card.
- Display Problems: If the display isn’t working correctly, check connections, resolution settings, and the graphics card’s driver status. Update the driver if needed.
- Driver Issues: If drivers are not functioning correctly, uninstall the old drivers and install the latest version of the appropriate driver from the manufacturer’s website. Check for compatibility issues with your operating system.
- Compatibility Issues: If there are compatibility issues, check the manufacturer’s specifications and make sure the new graphics card is compatible with the rest of your system components.
Updating Graphics Card Drivers
Upgrading drivers is a crucial step for optimal performance and stability. This ensures that the operating system can interact with the graphics card efficiently.
Drivers are essential software components that enable the operating system to communicate with hardware devices, like graphics cards.
- Download the Latest Drivers: Download the latest graphics card drivers from the manufacturer’s website. Ensure the drivers are compatible with your operating system version.
- Uninstall Existing Drivers: Uninstall any existing graphics card drivers before installing the new ones to prevent conflicts.
- Install the New Drivers: Follow the installation instructions provided with the drivers. This typically involves running the downloaded installer file.
- Restart the System: Restart your computer after installing the drivers to allow the changes to take effect.
System Configuration and Optimization
Completing the graphics card upgrade involves more than just installation. Proper system configuration and optimization unlock the full potential of your new hardware. This section details crucial steps to ensure optimal performance and stability.A well-configured system leverages the graphics card’s capabilities, delivering enhanced visual fidelity and smoother gameplay. Effective driver management and power settings are critical for maintaining stability and preventing performance bottlenecks.
Optimizing Operating System Settings
Proper configuration of operating system settings can significantly impact the graphics card’s performance. Adjusting display settings, resolution, refresh rate, and other visual parameters can enhance the visual experience and reduce potential issues.
Driver Updates
Driver updates are paramount for ensuring compatibility and optimal performance with the new graphics card. Outdated drivers can lead to instability, performance degradation, and compatibility issues with specific applications.
- Importance of Regular Updates: Regular driver updates are crucial. Manufacturers frequently release updates addressing performance bottlenecks, fixing bugs, and improving compatibility with newer hardware and software. This ensures the latest features and bug fixes are incorporated, enhancing overall system stability and performance.
- Checking for Updates: Most graphics card manufacturers provide utility software for automatic driver updates. Utilize this software for the most efficient way to stay up-to-date. Alternatively, manually checking the manufacturer’s website for updates is also an option. Verify the driver compatibility with your specific graphics card model to avoid potential issues.
- Installation Procedure: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the updated drivers. Carefully review the installation process to avoid any errors that could compromise system stability. Reboot the system after installation to ensure the changes take effect.
Utilizing Performance Monitoring Software
Dedicated software tools provide valuable insights into the graphics card’s performance. Monitoring metrics like frame rates, temperatures, and power consumption allows for proactive identification and resolution of potential bottlenecks.
- Monitoring Tools: Various tools are available, such as MSI Afterburner, RivaTuner Statistics Server (RTSS), or dedicated software from the graphics card manufacturer. These tools provide real-time feedback on crucial performance indicators, enabling adjustments to maximize performance while maintaining stability.
- Performance Metrics: These tools often display frame rates, temperatures, clock speeds, and other essential metrics. Observing these metrics allows users to identify performance bottlenecks, enabling optimization of the system configuration.
- Diagnostic Capabilities: Utilizing these tools allows for precise identification of potential issues. Users can monitor the graphics card’s performance under various workloads, allowing them to pinpoint specific bottlenecks or areas for improvement.
Power Settings Management
Managing power settings for the graphics card can significantly impact its performance and longevity. Carefully adjusting these settings allows for optimal performance and energy efficiency.
- Adjusting Power Limits: Some software allows adjustment of the power limits for the graphics card. Carefully consider the potential impact of increasing power limits on the graphics card’s temperature and overall system stability. Overclocking might be an option, but ensure that the cooling system is sufficient to handle the increased power draw.
- Balancing Performance and Power Consumption: Finding the balance between maximum performance and energy efficiency is critical. Lower power settings can lead to decreased performance, while excessively high settings might strain the graphics card and potentially lead to overheating. Carefully evaluate the impact of various settings on both performance and temperature.
Monitoring Temperatures and Cooling Solutions
Maintaining optimal temperatures is critical for the graphics card’s longevity and performance. Overheating can lead to performance degradation, stability issues, and even permanent damage.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitoring tools provide real-time feedback on the graphics card’s temperature. Regular monitoring allows for proactive identification and resolution of potential cooling issues. Pay close attention to the graphics card’s temperature during demanding tasks to prevent overheating.
- Cooling Solution Assessment: Ensure that the cooling solution is adequate for the new graphics card. If necessary, upgrade the cooling solution to prevent overheating. Factors like airflow, heatsink size, and fan performance are crucial considerations.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Maintaining your newly upgraded graphics card is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Proper troubleshooting and preventative maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of your hardware and prevent unexpected issues. This section Artikels strategies for diagnosing, resolving, and preventing common problems.Effective troubleshooting requires a systematic approach. Understanding the potential causes of problems is the first step in finding solutions.
This includes considering hardware compatibility, software conflicts, and environmental factors. A thorough understanding of your system’s components and how they interact is essential.
Diagnosing Graphics Card Issues
Troubleshooting graphics card problems often begins with careful observation and systematic elimination of potential causes. Identifying the source of the issue is vital for implementing the correct solution. Common problems include display issues, performance degradation, and unexpected shutdowns. Start by checking for physical damage to the card and the surrounding components. Next, review system logs for error messages.
Checking for Physical Damage
Visual inspection is the first step in assessing physical damage. Carefully examine the graphics card for any signs of bending, cracks, or loose components. Inspect the card’s connections, including the PCI Express slot, for any signs of damage or corrosion. If you suspect damage, consult the manufacturer’s documentation for guidance. Avoid forcing connections or components, as this could worsen the issue.
Identifying and Correcting Display Output Problems
Display output problems can stem from various factors. First, verify that the monitor is properly connected to the graphics card and powered on. Next, check the display settings in your operating system to ensure that the correct resolution and refresh rate are selected. If these steps don’t resolve the issue, consider updating the graphics card drivers. Ensure the drivers are compatible with your operating system and graphics card model.
Cleaning and Maintaining the Graphics Card
Regular cleaning is essential to prevent dust buildup and overheating. Use a can of compressed air to carefully remove dust and debris from the graphics card and surrounding components. Avoid using liquids or abrasive materials, as these can damage the components. Ensure that the fan is functioning properly and free of obstructions. If necessary, consult the manufacturer’s documentation for specific cleaning instructions.
A well-maintained graphics card runs cooler and more efficiently.
Routine Maintenance Checklist
Implementing a regular maintenance schedule is key to preventing future problems. This checklist provides a structured approach to keeping your system in optimal condition.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the graphics card and surrounding components for any signs of physical damage or dust accumulation. Pay particular attention to the cooling fans and heat sinks.
- Dust Removal: Use compressed air to remove dust and debris from the graphics card and surrounding components. Ensure you are using a safe method and not damaging any components.
- Driver Updates: Keep your graphics card drivers updated to ensure compatibility with your operating system and resolve any potential issues.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitor the temperature of your graphics card to ensure it is operating within safe limits. If the temperature is consistently high, consider improving cooling solutions.
- Software Optimization: Optimize your system software to ensure smooth operation and prevent resource conflicts.
Last Word

In conclusion, upgrading your graphics card is a rewarding experience, but it requires meticulous planning and execution. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can ensure a safe and successful upgrade. From meticulous pre-upgrade assessments to post-installation verification, this guide provides a comprehensive resource to maximize your investment and ensure optimal performance. Remember to prioritize safety and take your time to avoid costly mistakes.
Enjoy your newly enhanced visual experience!