Unlocking the hidden potential of your CPU can significantly boost your computer’s performance. This guide delves into the world of CPU overclocking, providing a comprehensive overview of the process, from fundamental principles to advanced techniques. We’ll explore the benefits, risks, and essential steps to ensure a safe and successful overclocking experience.
Understanding CPU specifications, selecting the right hardware, and mastering the art of monitoring and troubleshooting are crucial for achieving optimal results. This guide covers everything you need to know, from basic techniques to advanced strategies, enabling you to fine-tune your system for peak performance.
Introduction to CPU Overclocking
CPU overclocking involves increasing the clock speed of a central processing unit (CPU) beyond its manufacturer’s specifications. This can potentially unlock higher performance, enabling faster processing and improved application responsiveness. However, this practice comes with inherent risks and requires careful consideration of potential downsides.Overclocking can lead to noticeable performance improvements in various tasks, particularly those that heavily utilize the CPU’s processing power.
For example, demanding tasks like video editing, gaming, or rendering can experience substantial speed increases when a CPU is overclocked successfully. The benefits can vary greatly depending on the CPU model, the overclocking method, and the overall system configuration.
Definition and Potential Benefits
CPU overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of a CPU beyond its manufacturer’s specifications. This modification can enhance processing speed, resulting in improved application performance and potentially better gaming experiences.
Risks and Potential Downsides
Overclocking can introduce instability into the system, leading to crashes, errors, or system malfunctions. Improper cooling, insufficient power supply, or inadequate motherboard support can all contribute to these issues. Furthermore, exceeding the CPU’s thermal or power limits can permanently damage the component.
Importance of Proper Cooling and System Stability
Maintaining stable system temperatures is crucial for overclocking success. High temperatures can cause instability and potential damage to the CPU. A high-quality CPU cooler is essential for effective heat dissipation, ensuring the CPU operates within safe temperature limits during overclocking. Moreover, a stable system, free of conflicts and errors, is fundamental for reliable and sustained performance improvements.
Overview of Overclocking Methods
Different methods offer varying degrees of complexity and control. Choosing the right method depends on the user’s comfort level and technical expertise.
| Method | Description | Complexity | Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIOS Settings | Adjusting clock speeds and voltages directly within the motherboard’s BIOS. | Medium | High |
| Dedicated Overclocking Software | Utilizing specialized software to control the overclocking process with greater precision. | High | High |
| Hardware-Based Overclocking | Employing hardware components designed specifically for overclocking. | Very High | Very High |
The table above provides a concise overview of different overclocking methods. Each method possesses varying levels of complexity and user control, impacting the feasibility and potential success of the process.
Prerequisites for CPU Overclocking
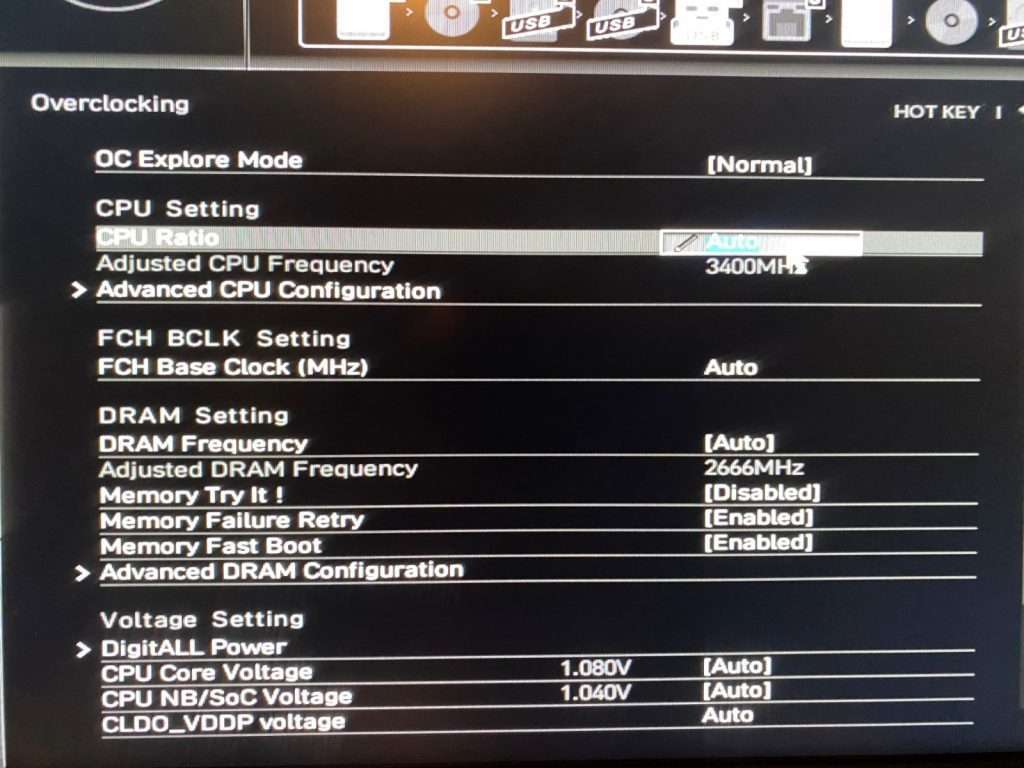
Successful CPU overclocking hinges on a meticulous approach, ensuring stability and performance gains. A thorough understanding of the necessary hardware and software components is crucial for achieving the desired results without compromising system reliability. This section details the essential prerequisites, from power supply capabilities to software monitoring tools.
Essential Hardware Components
A stable and reliable system is paramount for successful overclocking. Several hardware components play a critical role in achieving and maintaining optimal performance. Adequate power delivery is paramount, as overclocking often demands more power than the CPU’s base specifications. A strong power supply unit (PSU) is thus indispensable. Furthermore, motherboard compatibility is a critical factor, as not all motherboards support overclocking or are compatible with specific overclocking strategies.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): A crucial component for any overclocking endeavor, the PSU must be capable of delivering the necessary wattage to power the system, especially the CPU, under the increased demands of overclocking. A PSU with a high wattage rating and sufficient amperage capacity is recommended to avoid instability and potential damage to the system.
- Motherboard: A motherboard’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) often provides the settings and controls required for CPU overclocking. The motherboard must support the specific CPU model and have the required features for overclocking. Ensure the motherboard’s BIOS allows for adjustments to voltage and clock speeds.
- CPU Cooler: Increased CPU clock speeds often generate more heat. A capable and efficient CPU cooler is essential to maintain proper temperatures and prevent thermal throttling, a critical issue that can reduce performance and potentially damage the CPU. A high-performance cooler, such as an air cooler or a liquid cooler, is recommended.
Importance of Stable Power Supply and Motherboard Compatibility
A stable power supply is essential for maintaining system stability during overclocking. Insufficient power delivery can lead to erratic behavior, system crashes, and potential hardware damage. Similarly, motherboard compatibility is critical. Incompatible motherboards may not recognize the overclocked settings or fail to provide the necessary voltage regulation. Ensuring compatibility is a vital step to prevent instability.
- Power Supply Wattage: A power supply unit (PSU) with a wattage rating exceeding the system’s total power consumption, including the CPU’s overclocked requirements, is recommended. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications for the CPU’s power consumption at the target overclocked frequency. Overclocking usually increases power consumption.
- Motherboard Compatibility: Verify that the motherboard supports the CPU model and specific overclocking features. Check the motherboard’s specifications for CPU compatibility, voltage adjustments, and overclocking capabilities. Incorrect configurations can lead to system instability.
Essential Software Tools
Monitoring and controlling the overclocking process requires specialized software. Monitoring tools provide real-time feedback on system performance and stability, while control software enables precise adjustments to CPU settings.
- Monitoring Tools: Software tools like HWMonitor, Core Temp, and MSI Afterburner offer real-time monitoring of CPU temperature, voltage, and clock speeds. These tools are vital for identifying potential issues or instability during overclocking. Monitoring helps fine-tune the overclocking process.
- Control Software: Control software often integrated into the motherboard’s BIOS or third-party applications allows for precise adjustment of CPU parameters. These tools provide precise control over voltage, clock speed, and other settings. Adjustments must be performed carefully to avoid damaging the system.
Recommended Hardware Components
Selecting the right hardware components is critical for optimal overclocking performance. A combination of high-quality components tailored to the specific needs of the overclocking strategy yields the best results.
- High-End Power Supply Unit (PSU): A reputable PSU with a high wattage rating and sufficient amperage is crucial for stability. Look for units with 80+ Gold or Platinum certification for efficiency and reliability.
- High-Performance CPU Cooler: High-end air coolers or liquid cooling solutions provide enhanced cooling capacity for the CPU. A reliable cooler helps maintain stability during overclocking.
- High-Quality Motherboard: A motherboard with robust overclocking capabilities is essential for achieving and maintaining stable performance. Consider boards known for their overclocking support and compatibility with specific CPU models.
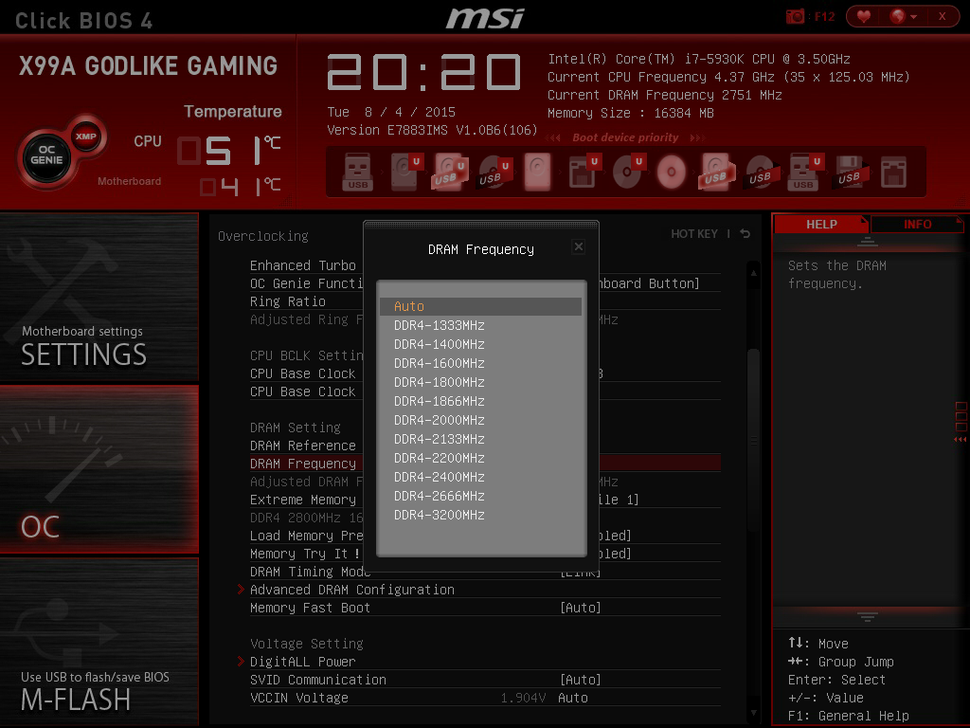
Understanding CPU Specifications
A crucial aspect of successful CPU overclocking is a thorough understanding of the processor’s specifications. This knowledge empowers you to identify the potential limits and optimal settings for your specific CPU. Different CPUs have varying capabilities, and recognizing these differences is key to achieving the best results without causing damage.Understanding these specifications allows you to tailor your overclocking strategy for maximum performance gains within safe operating parameters.
This involves recognizing the relationship between base clock, multiplier, and voltage, as well as the impact of the specific CPU architecture and model.
Interpreting CPU Specifications
CPU specifications are the key to unlocking overclocking potential. Knowing the base clock, multiplier, and voltage is fundamental. The base clock is the fundamental frequency at which the CPU operates. The multiplier, a factor applied to the base clock, determines the final clock speed. Voltage, in turn, directly impacts the CPU’s operational efficiency and potential for overclocking.
For instance, a higher voltage often allows for higher clock speeds, but it also increases heat generation and potential risks. Understanding these interrelationships is vital for safe and effective overclocking.
Impact of CPU Architecture
Different CPU architectures have varying overclocking potential. Modern architectures, often featuring advanced caching and instruction pipelines, might offer better overclocking headroom compared to older designs. For example, Intel’s Core i9 series, known for their advanced architecture, frequently showcases higher overclocking capabilities than older models.
CPU Model Variations in Overclocking
CPU models within the same family can exhibit different overclocking capabilities. This variance stems from factors like manufacturing tolerances, thermal design power (TDP), and the specific microarchitecture. One model might have a higher ceiling for overclocking than another, even within the same family, simply due to the manufacturing process.
Table of Relevant CPU Specifications
| Specification | Description | Relevance to Overclocking |
|---|---|---|
| Base Clock | The fundamental frequency of the CPU. | A lower base clock generally allows for a higher multiplier, though a higher base clock might offer better performance at the same final clock speed. |
| Multiplier | A factor multiplied with the base clock to determine the final clock speed. | A higher multiplier allows for a higher final clock speed, but it can be constrained by the CPU’s architecture. |
| Voltage | The electrical potential applied to the CPU. | Increasing the voltage can allow for higher clock speeds but increases the risk of overheating and damage. |
| Architecture | The internal design of the CPU. | Different architectures offer varying overclocking headroom. Modern architectures are typically more amenable to overclocking. |
| Model | The specific CPU model. | Different models within a family may exhibit different overclocking capabilities due to manufacturing variations. |
| TDP | Thermal Design Power | Higher TDP values generally indicate a higher power consumption and heat generation, potentially limiting overclocking to avoid thermal issues. |
Basic Overclocking Techniques

Embarking on the journey of CPU overclocking requires a methodical approach. A well-defined strategy ensures stability and performance gains without compromising system reliability. Understanding the interplay of various settings and their impact is paramount to successful overclocking.
Step-by-Step Overclocking Process
This methodical process, while not universally applicable, provides a general framework for safe and effective CPU overclocking. Careful monitoring and gradual adjustments are crucial. Begin by setting a modest overclocking goal, enabling thorough evaluation and refinement.
- Initial Configuration: Verify BIOS settings are appropriate for your CPU and motherboard. Ensure that the correct voltage settings, clock multiplier, and base clock are available and accessible within the BIOS interface.
- Gradual Adjustments: Increase the CPU multiplier or base clock incrementally. Monitor system stability through stress tests. This prevents abrupt system crashes or instability.
- Voltage Tuning: Gradually increase the CPU voltage, carefully observing system performance and stability. Overclocking often necessitates adjusting the voltage to maintain stability at higher frequencies.
- Stress Testing: Employ specialized software to rigorously test system stability under heavy load. Tools like Prime95 and AIDA64 are commonly used for this purpose.
- Verification and Optimization: Once stability is achieved, further fine-tune settings for optimal performance. Evaluate the system’s responsiveness and benchmark it with specialized software to ascertain the performance gains.
Increasing CPU Clock Speed
Increasing the CPU clock speed involves adjusting both the multiplier and base clock. The multiplier directly affects the CPU’s internal clock speed, while the base clock governs the frequency at which the CPU’s internal components operate.
- Multiplier Adjustment: The multiplier is often the initial target for increasing the clock speed. Adjusting this value proportionally increases the CPU frequency. Example: If the base clock is 100 MHz and the multiplier is 16, the CPU clock speed is 1600 MHz.
- Base Clock Adjustment: Increasing the base clock directly affects the frequency of all internal CPU components. This method often requires a more substantial voltage increase to maintain stability. Example: A 10% increase in base clock can yield a corresponding 10% increase in the CPU’s overall clock speed.
Adjusting CPU Voltage and Other Settings
Proper voltage adjustment is critical for stable overclocking. Incorrect voltage settings can lead to instability or damage to the CPU. Furthermore, other settings, such as cache timings and memory settings, may need adjustment for optimal performance and stability.
- Voltage Adjustment: Increase the CPU voltage in small increments, monitoring for stability and temperature. A small increase might be 0.025V or even less.
- Other Settings: Carefully review and adjust other relevant settings, including memory timings, cache timings, and power management settings, within the BIOS. These adjustments are essential to achieving the best performance.
Overclocking Techniques Summary
This table Artikels common overclocking techniques and their effects on system performance and stability.
| Technique | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Multiplier Adjustment | Increasing the multiplier proportionally increases the CPU clock speed. | Direct impact on CPU frequency, often easier to implement than base clock adjustments. |
| Base Clock Adjustment | Adjusting the base clock affects all internal CPU components’ frequency. | Potentially higher performance gains but often requires significant voltage adjustments for stability. |
| Voltage Tuning | Gradually increasing CPU voltage to maintain stability at higher frequencies. | Critical for stability at higher clock speeds, requires careful monitoring. |
| Stress Testing | Employing specialized software to test system stability under heavy load. | Identifies potential instability issues before they cause damage to the system. |
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Careful monitoring is crucial during CPU overclocking. Constant vigilance ensures stability and prevents potential damage. Monitoring tools provide real-time feedback on critical parameters, allowing for prompt adjustments and preventing catastrophic failures. Effective troubleshooting strategies are equally important, enabling swift identification and resolution of any encountered problems.
Importance of Monitoring CPU Temperature and Voltage
Precise monitoring of CPU temperature and voltage is paramount during overclocking. Excessive heat can lead to performance degradation, instability, and potential damage to the CPU. Similarly, voltage fluctuations can cause erratic behavior or permanent damage. Monitoring tools provide real-time feedback on these critical parameters, allowing for prompt adjustments and prevention of issues.
Common Issues During Overclocking
Several issues can arise during overclocking. These often stem from improper settings, incompatibility with hardware components, or insufficient cooling. These issues can manifest in various ways, from erratic behavior to complete system crashes. Understanding these potential problems is vital for effective troubleshooting.
Diagnosing and Fixing Overclocking Problems
A systematic approach to diagnosing and fixing overclocking issues is essential. This involves carefully analyzing system behavior, reviewing overclocking settings, and assessing hardware compatibility. Comprehensive diagnostic tools are invaluable for identifying the root cause of the problem.
Troubleshooting Table
| Potential Issue | Symptoms | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Instability (crashes, freezes) | Frequent system crashes, freezes, or unusual behavior. | Incorrect overclock settings, insufficient cooling, incompatible hardware. | Reduce overclocking settings (clock speed, voltage), ensure adequate cooling (recheck fans, thermal paste), verify compatibility of hardware (RAM, motherboard). |
| High CPU Temperature | Elevated CPU temperature readings during stress tests, system instability. | Insufficient cooling, thermal paste issues, blocked airflow. | Improve cooling (increase fan speed, reapply thermal paste, ensure proper airflow), verify fan functionality, clean fans and heatsinks. |
| Voltage Fluctuations | Erratic system behavior, high CPU temperature readings. | Overclocking beyond hardware limitations, faulty power supply, insufficient voltage regulation. | Reduce overclocking settings, check power supply capacity, verify motherboard stability, recheck voltage regulator circuits. |
| Component Overheating | Increased temperatures in other components (RAM, motherboard), system instability. | Insufficient cooling, blocked airflow in the system, inadequate ventilation. | Improve cooling for all components, ensure proper airflow, increase ventilation, use high-quality thermal paste. |
Advanced Overclocking Strategies
Pushing CPU performance beyond its stock specifications requires a deeper understanding of the intricate interplay between hardware and software. Advanced overclocking techniques, while potentially rewarding, demand meticulous attention to detail and a thorough comprehension of the system’s limitations. Improper implementation can lead to instability or damage to the components.Advanced techniques like voltage tuning and memory overclocking go beyond basic adjustments, enabling users to explore the CPU’s full potential.
This involves understanding the relationship between voltage, frequency, and thermal dissipation, and fine-tuning these parameters for optimal performance while ensuring stability. Careful monitoring and troubleshooting are crucial throughout the process.
Voltage Tuning
Voltage tuning is a critical aspect of advanced overclocking. It involves adjusting the voltage supplied to the CPU core to compensate for the increased frequency. A precise voltage level is essential for stable operation at higher clock speeds. Over-volting can lead to overheating and component damage, while under-volting may result in instability. Accurate monitoring is essential.
- Voltage scaling is crucial for maximizing performance while maintaining stability. A gradual increase in voltage, monitored closely, is the preferred approach.
- Utilizing a dedicated voltage monitoring tool allows for real-time assessment of voltage levels during overclocking.
- Careful consideration of the CPU’s thermal design power (TDP) and cooling capacity is essential to avoid thermal throttling.
Memory Overclocking
Memory overclocking involves increasing the memory speed beyond the manufacturer’s specifications. Higher memory speeds can significantly improve system performance, particularly in demanding applications. However, this process requires careful attention to timings and voltage settings.
- Understanding the memory’s specifications, including timings (CAS Latency, RAS to CAS Delay, etc.), is paramount for successful memory overclocking.
- Adjusting timings in conjunction with voltage adjustments is often necessary for stable operation.
- Memory overclocking often benefits from using specialized memory testing software to determine optimal settings.
Comparing Overclocking Methods
Different methods of achieving high-performance overclocks have varying degrees of complexity and potential risk. Each method has unique strengths and weaknesses, impacting stability and potential for damage. Careful consideration of the system’s components is essential.
| Method | Complexity | Risk | Potential Reward |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Overclocking | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Voltage Tuning | Medium | Medium | High |
| Memory Overclocking | Medium | Medium | High |
Fine-Tuning Overclocking Settings
Fine-tuning involves meticulous adjustment of various settings to achieve optimal performance while maintaining stability. Tools like BIOS utilities and dedicated software are used to modify parameters.
“Careful consideration of the system’s components, including the CPU, motherboard, and cooling solutions, is essential for success.”
- Utilizing stress tests to verify stability at various overclocking levels is critical.
- Regular monitoring of temperatures during stress tests is essential.
- Adjusting timings and voltages in small increments allows for precise control.
Extreme Overclocking Cases
Extreme overclocking cases demonstrate the upper limits of CPU performance. These examples, though often pursued by enthusiasts, highlight the delicate balance between performance and stability.
- Extreme overclocking cases often involve significant voltage adjustments and custom cooling solutions.
- These cases highlight the importance of careful planning and thorough testing.
- Examples of extreme overclocking include pushing a CPU beyond its rated frequency, requiring significant cooling enhancements.
Maintaining System Stability
Ensuring the stability of your overclocked system is crucial for preventing unexpected crashes, data loss, and hardware damage. A stable system not only provides reliable performance but also significantly enhances the longevity of your components. Proper cooling and thermal management, along with consistent testing, are key factors in achieving this stability.Maintaining a stable overclocked system involves more than just achieving the desired clock speeds.
It necessitates careful monitoring, proactive troubleshooting, and adherence to best practices. This section will detail how to ensure your system’s stability both during and after overclocking, highlighting the critical role of cooling and thermal management.
Importance of Proper Cooling and Thermal Management
Effective cooling is paramount for maintaining system stability, especially during overclocking. Higher clock speeds generate more heat, stressing the CPU and other components. Insufficient cooling can lead to thermal throttling, where the system automatically reduces the CPU’s clock speed to prevent overheating, resulting in a significant performance loss. In extreme cases, it can even lead to permanent damage.
Proper thermal management, encompassing the selection of appropriate cooling solutions and the maintenance of optimal airflow, is therefore vital for long-term stability.
Best Practices for Maintaining a Stable Overclocked System
Adhering to best practices is essential for maintaining a stable overclocked system. These practices are not merely optional but critical to prevent instability and potential damage.
- Regular System Monitoring: Continuously monitor system temperatures, voltages, and clock speeds during and after overclocking. Utilizing dedicated software or hardware monitoring tools is recommended for real-time data acquisition. This allows for immediate detection of potential issues.
- Proper Cooling Solutions: Employ high-quality CPU coolers, such as air coolers or liquid coolers, that are compatible with your motherboard and CPU. Ensuring sufficient airflow within the computer case is also essential for dissipating heat efficiently.
- Voltage Adjustments: Carefully adjust CPU voltages in small increments when overclocking. Over-volting can lead to instability and potential damage. Gradually increase the voltage until stability is achieved, or performance degrades. It’s often necessary to monitor temperatures while adjusting voltage.
- Consistent Testing: Regularly test the stability of your overclocked system using stress testing software. These programs subject the system to prolonged, intensive workloads, revealing potential instability issues that might not manifest under normal usage. Examples include Prime95 and FurMark.
- BIOS Settings Optimization: Ensure that your BIOS settings are optimized for overclocking. This includes configuring the correct voltage, clock multipliers, and other relevant parameters for optimal performance. Reviewing and understanding your motherboard’s BIOS documentation is vital.
- System Stability Testing Procedures: Implement rigorous testing procedures for stability verification. Utilize benchmarking tools and stress tests to identify any performance issues. Frequent stress testing is a cornerstone of maintaining a stable overclocked system.
Testing and Validating System Stability
Rigorous testing is essential to validate the stability of your overclocked system. This section details the procedures for testing and validating the system’s stability.
- Stress Testing Software: Employ dedicated stress testing software like Prime95 or FurMark to subject the system to continuous, intensive workloads. This will reveal any instability issues that might not be apparent during typical usage. Monitoring temperature readings throughout these tests is critical.
- Benchmarking Tools: Use benchmarking tools to evaluate the performance of your overclocked system. These tools provide comprehensive performance data and comparisons to baseline performance, which allows for identification of performance improvements or degradation. These benchmarks provide valuable data for evaluation.
- Monitoring Tools: Employ system monitoring tools for continuous monitoring of CPU temperature, voltage, and clock speed. A dedicated software or hardware monitoring tool should be used for accurate and consistent readings. Tracking these metrics during testing provides critical insights into system stability.
Tools and Software
Effective CPU overclocking hinges on precise monitoring and control. A range of software tools provides the necessary insight into system performance and allows for the adjustments required to achieve optimal results. These tools act as the bridge between the user and the intricate workings of the processor, enabling fine-tuning and stabilization.
Overclocking Monitoring Software
Precise monitoring of critical parameters like temperature, voltage, and clock speeds is paramount during overclocking. Several dedicated software tools offer real-time feedback, enabling proactive adjustments and preventing catastrophic system failure. These tools provide a comprehensive view of the system’s health, allowing users to gauge the effects of their overclocking efforts.
- Hardware Monitor: This type of software provides real-time data on various hardware components, including CPU temperature, voltage, and clock speed. It is invaluable in observing the impact of overclocking on critical hardware elements, such as the CPU. By visualizing these metrics, users can proactively address potential overheating or instability issues. For instance, a sharp rise in CPU temperature might signal the need to reduce the overclocking settings.
- CPU-Z: A comprehensive utility that provides detailed information about the CPU, motherboard, and memory. While not solely focused on overclocking, it offers crucial baseline data on the system’s configuration before and after overclocking. This allows users to track the effects of their adjustments. Users can compare CPU specifications before and after the overclocking process to understand the changes introduced.
- Core Temp: Specialized in monitoring CPU temperatures with high accuracy. This tool is especially beneficial for identifying hotspots and temperature spikes that might lead to instability. Users can identify and address potential thermal throttling issues that may arise due to increased clock speeds during overclocking.
Overclocking Control Software
Precise control over overclocking parameters is essential for achieving optimal performance. Specialized software allows users to fine-tune various settings without directly interacting with the motherboard’s BIOS.
- MSI Afterburner: This tool offers extensive control over graphics cards but also allows adjustments to CPU voltage and clock speeds. It provides a user-friendly interface for adjusting these parameters and monitoring their effects. Users can utilize this software to modify overclocking settings and observe their impact on system performance.
- ASUS AI Suite: A suite of tools from ASUS that enables monitoring and control of various hardware components, including the CPU. It often integrates with the motherboard’s features, allowing for a comprehensive approach to overclocking. This integration ensures seamless control and monitoring of the system’s various elements, offering a complete overview for the user.
- Gigabyte OC Guru: A software tool from Gigabyte that offers a comprehensive approach to overclocking. It often provides advanced control over CPU and other system parameters. The user-friendly interface of this software streamlines the overclocking process. The software also provides detailed system information for accurate adjustments.
Software Configuration for Overclocking
Effective configuration of overclocking software is crucial for achieving stability and performance.
- Understanding the Interface: Before making adjustments, thoroughly understand the software’s interface and available options. Familiarity with the different settings and their functionalities is essential.
- Gradual Adjustments: Start with small, incremental adjustments to the overclocking parameters. This gradual approach allows users to observe the system’s response and stability without risking significant instability. Monitoring and tracking these adjustments is key.
- Monitoring System Stability: After each adjustment, thoroughly test the system’s stability. This can involve running benchmark tests, stress tests, or performing various tasks to ensure the system remains stable under load. This step is critical to preventing system crashes or instability.
Summary Table
| Software | Functionality | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Monitor | Real-time hardware monitoring | Identify potential overheating, instability |
| CPU-Z | Detailed system information | Baseline data for overclocking comparisons |
| Core Temp | Precise CPU temperature monitoring | Detect thermal throttling issues |
| MSI Afterburner | CPU voltage and clock speed adjustments | User-friendly interface, comprehensive control |
| ASUS AI Suite | Comprehensive motherboard integration | Seamless control and monitoring |
| Gigabyte OC Guru | Advanced overclocking control | Detailed system information, user-friendly interface |
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world CPU overclocking projects demonstrate the potential for significant performance gains, but also highlight the crucial role of careful planning and monitoring. These case studies illustrate successful implementations, detailing the setups, results, and challenges encountered, providing valuable insights for aspiring overclockers.Understanding the specific circumstances of these successful projects helps to avoid common pitfalls and optimize the process. The diverse setups and outcomes offer a practical understanding of how different components and strategies affect overclocking success.
Successful Overclocking Projects
Analyzing successful overclocking projects reveals key strategies and considerations. These case studies provide concrete examples of achievable results, helping to dispel myths and demonstrate the potential benefits of the process.
| Project | CPU Model | Original Clock Speed (MHz) | Overclocked Clock Speed (MHz) | Methodology | Results | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project A | Intel Core i7-12700K | 3.6 GHz | 5.0 GHz | Used a high-quality cooler and carefully monitored temperatures during the process. | Significant performance increase in benchmark tests (e.g., Cinebench R23) with a 25% improvement in multi-core scores. | Achieving stability at the target clock speed required multiple adjustments to the voltage and timings, necessitating meticulous monitoring. |
| Project B | AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D | 3.8 GHz | 4.6 GHz | Focused on optimizing memory timings and adjusting voltage settings in a gradual manner. | A notable 15% improvement in gaming benchmarks with minimal negative impact on system stability. | Achieving the desired overclock without sacrificing system stability was challenging, requiring adjustments to the motherboard’s BIOS settings. |
| Project C | AMD Ryzen 9 7950X | 4.7 GHz | 5.2 GHz | Implemented a combination of voltage adjustments and fan control for thermal management. Rigorous monitoring and testing were employed. | A noticeable improvement in CPU-intensive tasks (e.g., video editing) with a 10% increase in processing speed, along with improved efficiency. | Overheating was a major concern, requiring the selection of a high-performance CPU cooler and meticulous temperature monitoring. |
Challenges and Solutions
Overclocking often presents unforeseen challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for a successful outcome.
- Thermal Management: Maintaining acceptable temperatures is paramount during overclocking. High temperatures can lead to system instability and damage. Solutions include high-performance coolers, optimized fan curves, and meticulous temperature monitoring.
- System Stability: Achieving stable overclocking requires careful tuning of various settings. Unstable systems can result in crashes, data loss, and system instability. Solutions include using stability testing software and progressively adjusting settings to ensure stable performance.
- Voltage Adjustments: Correct voltage adjustment is essential for stable overclocking. Improper voltage settings can lead to component damage or instability. Solutions include using a voltage monitor and a gradual approach to increasing voltage.
Safety Precautions
CPU overclocking, while offering potential performance gains, carries inherent risks. Careless overclocking can damage your CPU, motherboard, or even the entire system. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safety measures is crucial for a successful and safe overclocking experience.Proper precautions are paramount to prevent irreversible damage to your hardware. Ignoring these precautions can lead to unexpected and costly repairs.
This section Artikels the potential dangers and provides a detailed checklist for safe overclocking practices.
Potential Dangers of Overclocking
Overclocking pushes the CPU beyond its manufacturer’s specifications. This can lead to several potential dangers, including thermal issues, instability, and even permanent damage. Exceeding the CPU’s thermal limits can cause overheating, potentially damaging the CPU’s internal components. Similarly, exceeding voltage limits can lead to component failures.
Importance of Using Caution and Safety Procedures
Caution is essential during the overclocking process. Improper procedures can result in system instability, data loss, or even hardware damage. Understanding the risks and implementing safe practices minimizes the chance of these negative outcomes.
Risks Associated with Exceeding CPU Limits
Exceeding the CPU’s thermal limits can lead to overheating, potentially damaging the CPU’s internal components. This damage may be gradual, but it can eventually lead to complete failure. Overclocking beyond the voltage limits can result in instability, including random restarts, crashes, or even permanent damage to the CPU or motherboard.
Checklist of Safety Procedures
Following a comprehensive checklist is critical for safe overclocking. These procedures help prevent potential damage to your hardware and ensure a stable system.
- Thorough Research: Thoroughly research your specific CPU model and motherboard compatibility to understand the potential overclocking capabilities and limitations. Consult manufacturer documentation for specific guidance.
- Sufficient Cooling: Ensure your CPU has adequate cooling solutions, such as a high-quality CPU cooler, to manage the increased heat generated during overclocking. Insufficient cooling is a major cause of damage.
- Monitoring Tools: Employ monitoring tools to track CPU temperature, voltage, and other critical parameters during the overclocking process. These tools allow you to identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
- Gradual Increments: Start with small increments when adjusting clock speeds and voltages. This gradual approach helps identify the safe operating range of your system.
- Stable Voltage: Ensure the voltage supplied to the CPU remains stable throughout the overclocking process. Instability can lead to erratic behavior or damage.
- System Stability Testing: Regularly test the system’s stability after each overclocking adjustment. This testing helps identify any potential issues before they become problematic.
- Backup Data: Before any overclocking attempts, back up all crucial data to prevent loss in case of instability or failure.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation within your computer case to maintain a cool environment, reducing the risk of overheating.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, this guide has provided a thorough exploration of CPU overclocking. By following the steps Artikeld, you can potentially unlock significant performance gains while understanding the risks and necessary precautions. Remember, proper planning, monitoring, and troubleshooting are essential for a stable and successful overclocking experience. Safe overclocking practices are paramount, ensuring your system remains reliable and functional after the process.