Welcome to a comprehensive guide on benchmarking your new PC’s performance. Understanding how your system performs is crucial for optimizing its capabilities and identifying potential bottlenecks. This guide will walk you through the entire process, from preparation to analysis, enabling you to fully leverage the power of your new machine. We’ll cover essential steps and techniques, ensuring you get the most out of your hardware.
This guide provides a structured approach to benchmarking, encompassing various aspects from initial setup to troubleshooting and optimization. It details different benchmarking tools, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to select the best one for your needs. Understanding your PC’s performance is paramount to maximizing its potential.
Introduction to Benchmarking PC Performance
PC performance benchmarking is a crucial process for evaluating and comparing the capabilities of a computer system. It involves running specialized software to measure various aspects of a computer’s performance, such as processor speed, memory bandwidth, and graphics rendering capabilities. These results provide a standardized metric to objectively assess the system’s overall speed and efficiency.Benchmarking helps identify the strengths and weaknesses of a new PC, enabling users to make informed decisions about its suitability for specific tasks or applications.
This process allows for objective comparisons between different configurations and assists in determining the optimal components for a given budget and workload.
Different Types of PC Performance Benchmarks
Benchmarking encompasses a wide array of performance tests. These tests measure various components and functionalities of a PC. Different types of benchmarks target different aspects, providing a comprehensive picture of the system’s capabilities. Processor benchmarks, for example, assess the CPU’s speed and efficiency in handling calculations. Memory benchmarks measure the speed and capacity of the system RAM.
Graphics benchmarks evaluate the capabilities of the graphics card in handling complex visual tasks. Storage benchmarks test the read and write speeds of the hard drive or SSD.
Importance of Benchmarking a New PC’s Performance
Benchmarking a new PC is essential for understanding its true capabilities and limitations. It provides objective data that allows for informed comparisons with other systems and configurations. This crucial data helps users ensure the system meets their needs. It is especially important when considering the budget and intended use cases. By identifying potential bottlenecks or weaknesses, users can optimize their system for optimal performance.
Overview of Common Benchmarking Tools and Software
Numerous benchmarking tools and software packages are available, catering to various needs and levels of expertise. These tools offer a wide range of tests and reports to comprehensively assess a system’s capabilities. Some popular choices include Cinebench, 3DMark, and PCMark. These programs run a series of tests, providing numerical results that can be compared and analyzed.
Comparison of Popular Benchmarking Software Packages
| Software | Strengths | Weaknesses | Supported Hardware |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cinebench | Excellent for CPU benchmarking, providing detailed results. Known for its accurate and consistent performance measurements. | Limited graphics card testing capabilities. May not comprehensively evaluate all system components. | Wide range of CPUs and systems. |
| 3DMark | Comprehensive graphics card benchmarking, providing realistic performance assessments. Wide range of tests covering different game scenarios. | May not be as accurate for CPU or storage benchmarking. Can be complex to interpret for users new to benchmarking. | Extensive support for modern GPUs and gaming hardware. |
| PCMark | Overall system performance benchmark. Provides a more holistic view of the system’s capabilities, including CPU, GPU, storage, and memory. Useful for comparing different configurations. | Might not provide as detailed results as specialized benchmarks for specific components. Tests may be less relevant for certain workloads. | Covers a broad spectrum of hardware and systems, including mobile devices. |
Preparing for the Benchmark

Thorough preparation is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable benchmark results. A well-prepared system ensures that the results reflect the true performance of the PC, free from extraneous factors. This section details the essential steps to achieve this.A meticulously prepared system minimizes external variables, allowing for a precise evaluation of the hardware’s capabilities. Understanding and addressing potential issues before commencing the benchmark is paramount for a robust and meaningful assessment.
Essential System Requirements for Accurate Benchmarking
Precise benchmarking demands a system configuration optimized for the task. This involves ensuring the system’s stability and eliminating potential sources of error. Sufficient system resources are necessary for the benchmark software to run smoothly without bottlenecks. Adequate RAM, free disk space, and sufficient processing power are critical for optimal results. A dedicated, unused portion of the hard drive is ideal to avoid interference from other applications.
Steps to Ensure a Stable and Optimized System for Benchmarking
A stable system environment is essential for accurate benchmark results. This involves minimizing background processes that might consume system resources and impact the performance evaluation.
- Disable unnecessary background applications: Applications running in the background can consume significant system resources, potentially affecting the benchmark results. Close unnecessary programs, including those running in the system tray, to ensure that the system resources are dedicated to the benchmark process. This includes disabling or minimizing the activity of antivirus software and other system utilities that might interfere with the benchmark.
- Close unnecessary browser tabs and windows: Active browser tabs and windows consume resources, impacting the overall performance of the system. Closing unnecessary tabs and windows minimizes the load on the system, ensuring a smoother benchmark execution.
- Run a full system scan (if needed): A full system scan can help eliminate any malware or corrupted files that could impact the performance of the PC. This step ensures that the system is clean before the benchmark process begins.
- Restart the system: A clean system boot ensures that the system is free from temporary files and processes that might interfere with the benchmark process. Restarting the system is a fundamental step in achieving a stable environment for benchmarking.
Importance of Clean System Boot for Reliable Results
A clean system boot is vital for obtaining accurate benchmark results. It ensures that the system is free from temporary files and processes that might interfere with the benchmark.
Necessary Hardware and Software for a Proper Benchmarking Setup
The required hardware and software should be sufficient to run the benchmark tests without any issues. A high-quality, stable internet connection is crucial if online benchmarks are used.
- Hardware: A stable power supply, a fast internet connection (if required by the benchmark software), and a high-performance CPU are crucial for consistent results. Sufficient RAM is essential to prevent performance bottlenecks. A dedicated, unused hard drive space for the benchmark process is highly recommended to avoid conflicts.
- Software: Select reputable benchmarking software from trusted sources, ensuring compatibility with the operating system and hardware configuration. Examples include 3DMark, Cinebench, and PCMark. Thorough research on the software is essential to ensure its compatibility with the PC’s specifications.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Installing and Configuring Benchmarking Software
The correct installation and configuration of the benchmarking software are essential for obtaining accurate results. Following a step-by-step process ensures a proper setup.
- Download the benchmarking software: Download the chosen benchmarking software from a reputable source to ensure its integrity and compatibility.
- Install the software: Install the software according to the instructions provided. Ensure to select the appropriate installation options for your system.
- Configure the software: Configure the software to run the specific tests required for the user’s needs. This step involves setting parameters such as resolution, graphics settings, and test duration.
Configuring Benchmarking Software to Run Tests Specific to User’s Needs
Tailoring the benchmark tests to the user’s specific needs enhances the relevance and accuracy of the results. This involves selecting appropriate settings and parameters within the software.
- Selecting test types: Benchmarking software often offers different test types, focusing on specific hardware components. Choosing the appropriate tests is crucial for a comprehensive analysis of the PC’s performance.
- Setting resolutions and graphics settings: Adjusting resolution and graphics settings within the benchmark software allows the user to simulate real-world usage scenarios and provide more accurate results.
- Defining test duration: Adjusting the test duration allows for a more in-depth assessment of the PC’s performance, particularly when focusing on stability.
Importance of System Stability Before Running Benchmarks
Ensuring system stability is essential for accurate benchmarking results. Any instability or interference can lead to inaccurate readings. A stable system environment guarantees a reliable evaluation of the PC’s performance.
Common Issues Affecting Benchmark Results and Solutions
Several factors can affect the accuracy of benchmark results. Addressing these issues can lead to more reliable evaluations.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| High CPU/GPU temperatures | Ensure adequate cooling (e.g., fans, cooling solutions) or reduce the test’s intensity. |
| Power fluctuations | Use a surge protector to stabilize the power supply. |
| Background processes | Close unnecessary applications and disable background processes. |
| System instability | Restart the system and ensure the system is running optimally. |
| Driver issues | Update drivers to the latest versions. |
Running the Benchmarks

Executing benchmark tests provides crucial insights into your new PC’s performance. This section details the various benchmark types, their execution, and example results, allowing you to effectively evaluate and compare different hardware components.
Different Benchmark Test Types
Understanding the different benchmark types is vital for a comprehensive performance assessment. Various tests focus on specific aspects of your system, ranging from CPU processing power to GPU graphical capabilities and RAM speed.
- CPU Benchmarks: These tests evaluate the central processing unit’s ability to handle complex tasks. They typically involve running mathematical calculations, sorting algorithms, or simulating real-world applications to measure the CPU’s speed and efficiency.
- GPU Benchmarks: These tests measure the graphics processing unit’s capabilities. They frequently involve rendering complex 3D scenes, applying various filters, and evaluating the GPU’s ability to manage graphical workloads. GPU benchmarks are crucial for gamers and professionals requiring high-quality visuals.
- RAM Benchmarks: These tests assess the speed and performance of the Random Access Memory. They focus on the time it takes to retrieve and store data in RAM, indicating the system’s ability to quickly access information. RAM benchmarks are essential for applications requiring significant memory usage, such as large video editing projects.
- Storage Benchmarks: These tests evaluate the performance of the storage devices (hard drives or solid-state drives). They measure the speed of reading and writing data, which directly impacts the loading times of games and applications.
Executing Benchmark Tests
Following specific steps is essential for accurate and reliable benchmark results. Each test requires particular configurations to avoid inaccurate readings.
- CPU Benchmark Execution: Download a suitable CPU benchmark tool, such as Cinebench or Geekbench. Run the benchmark according to the tool’s instructions. Ensure your system is stable and that other applications are closed to avoid interference. Repeat the test multiple times to obtain consistent results.
- GPU Benchmark Execution: Download a GPU benchmark tool, such as 3DMark or Unigine. Configure the test settings according to the specific needs and expectations. Run the test and observe the results carefully, noting any variations. Multiple runs are essential for reliable results.
- RAM Benchmark Execution: Download a RAM benchmark tool, such as Memtest86 or Everest. Follow the provided instructions to run the benchmark, ensuring your system is stable and all unnecessary programs are closed. Thorough RAM testing is vital for identifying potential stability issues.
- Storage Benchmark Execution: Use tools such as CrystalDiskMark or AS SSD to benchmark storage performance. Perform tests to assess sequential and random read/write speeds. Ensure the storage device is the primary boot drive to get the most accurate results.
Benchmark Test Results
Examples of benchmark test results for different components illustrate the significance of these tests.
| Component | Benchmark Tool | Score | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Cinebench R23 | 1500 | A high score indicates a powerful CPU capable of handling demanding tasks efficiently. |
| GPU | 3DMark Time Spy | 12000 | A high score suggests a robust GPU suitable for high-resolution gaming and demanding graphical applications. |
| RAM | Memtest86 | No Errors | Error-free results confirm the RAM’s stability and functionality. |
| Storage | CrystalDiskMark | Sequential Read: 550 MB/s | High sequential read speeds imply fast file access, crucial for loading large files quickly. |
Analyzing the Results
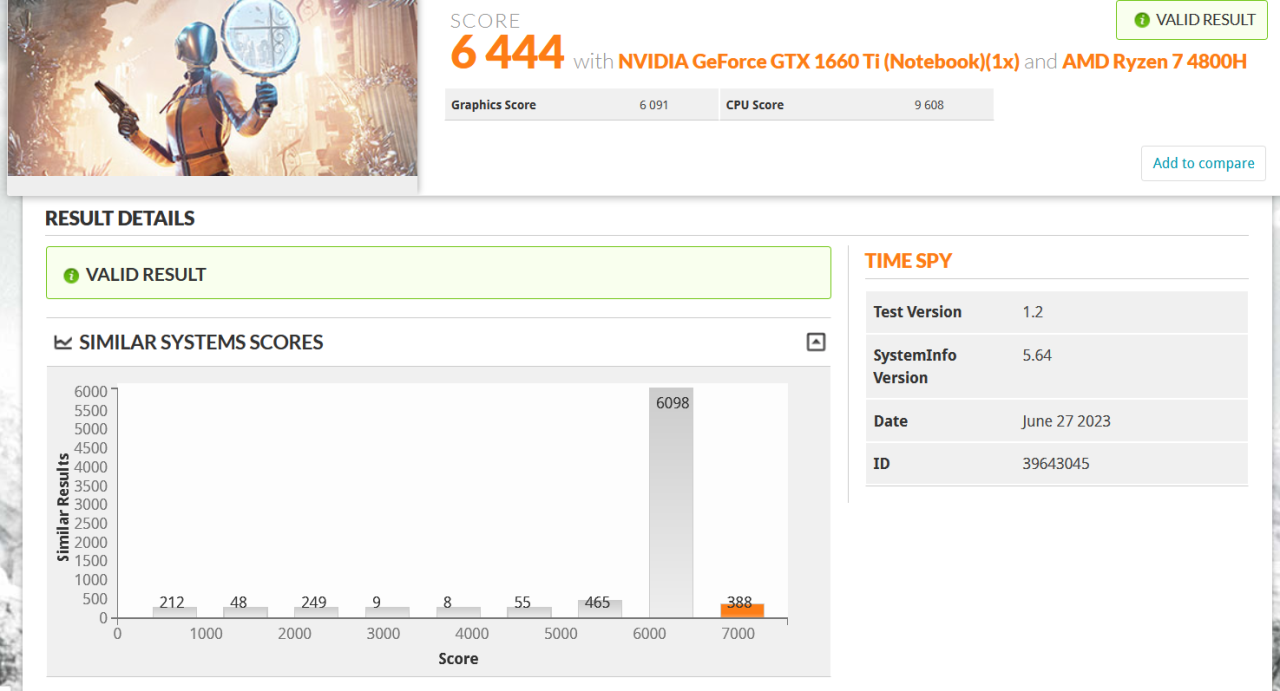
Interpreting benchmark results is crucial for understanding your PC’s performance strengths and weaknesses. A thorough analysis allows you to identify bottlenecks, fine-tune components, and ultimately optimize your system’s capabilities. This section provides a structured approach to interpreting benchmark results, pinpointing performance issues, and making informed decisions for system improvements.A key aspect of analyzing benchmark results is understanding the context.
Different benchmarks measure different aspects of performance. For instance, some benchmarks focus on CPU performance, while others evaluate GPU capabilities. Understanding the specific metrics and their implications is vital to properly assess the overall performance.
Interpreting Benchmark Scores
Benchmark scores provide numerical representations of a PC’s performance across various tasks. High scores generally indicate better performance, but the meaning is dependent on the specific benchmark and the context of the results. For example, a high score in a 3D rendering benchmark suggests a strong GPU, while a high score in a CPU benchmark indicates a powerful processor.
It’s important to analyze multiple benchmarks to gain a comprehensive understanding of the system’s performance.
Identifying Performance Bottlenecks
Identifying performance bottlenecks is a critical step in optimizing a system. Bottlenecks are components that limit the overall performance of the system. A benchmark’s breakdown of scores by component can help you pinpoint bottlenecks. For instance, if the CPU benchmark score is significantly lower than the expected score, it indicates a potential CPU bottleneck.
Troubleshooting and Fixing Performance Issues
Benchmark results offer clues to potential issues. If a specific benchmark shows lower-than-expected scores, it signals a potential problem that needs attention. For example, a low score in a memory benchmark could point to insufficient RAM or issues with RAM configuration. Troubleshooting involves investigating the suspected component and its configuration.
Comparing Results to Expected Performance
Comparing benchmark results with expected performance based on PC specifications is crucial for evaluation. Expected performance is estimated based on the specifications of the PC components. For instance, a high-end CPU should perform better in CPU benchmarks compared to a lower-end CPU. Any significant discrepancies can indicate potential hardware or driver issues.
Improving PC Performance Based on Results
Benchmark results offer valuable insights for system improvement. If a particular component shows a performance bottleneck, consider upgrading that component to enhance the overall system performance. For example, if the benchmark indicates a slow hard drive, upgrading to a solid-state drive (SSD) can significantly improve the system’s speed.
Creating a Clear Performance Report
A clear performance report is essential for documenting and analyzing the results. The report should include a summary of the benchmark scores, a breakdown of performance by component, identification of bottlenecks, and suggested solutions. This report serves as a valuable record for future system analysis and improvement.
Factors Influencing Benchmark Scores
Various factors influence benchmark scores, including the specific benchmark used, the hardware configuration, and the software environment. For example, different benchmarks may have different weights for various components. Furthermore, the presence of background processes and system load can significantly affect benchmark scores. Understanding these influencing factors allows for more accurate interpretation of the results.
Performance Component Analysis
| Component | Benchmark Score | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | High | Excellent processing power. |
| CPU | Low | Potential bottleneck. Consider upgrading. |
| GPU | High | Excellent graphics performance. |
| GPU | Low | Potential bottleneck in graphics-intensive tasks. Consider upgrading. |
| RAM | High | Efficient memory management. |
| RAM | Low | Potential bottleneck in memory-intensive tasks. Consider upgrading. |
| Storage | High | Fast data access. |
| Storage | Low | Slow data access. Consider upgrading to an SSD. |
This table provides a simplified illustration of how benchmark scores can be analyzed to identify potential issues and suggest solutions. Always consider the specific context of the benchmark and the PC’s configuration when interpreting these results.
Troubleshooting Performance Issues
Often, despite careful system configuration and component selection, unexpected performance issues can arise after building a new PC. Understanding the potential causes and implementing effective troubleshooting steps is crucial to identifying and resolving these problems. Benchmarks, while valuable, can sometimes be misleading, requiring a deeper investigation into the system’s health.Benchmark results may not always accurately reflect real-world performance due to various factors.
These include fluctuating system resources, background processes, and even the specific workload being tested. Consequently, inconsistent benchmark scores may point to underlying issues needing thorough diagnosis. A methodical approach to troubleshooting is essential to isolate the source of performance problems and restore optimal system operation.
Common Performance Issues
Several factors can contribute to suboptimal PC performance. These include issues with the operating system, hardware conflicts, insufficient system resources, and software applications consuming excessive resources. Understanding these potential problems is the first step toward effective troubleshooting.
Reasons for Inconsistent Benchmarks
Benchmark inconsistencies can stem from several factors. Variability in system resource allocation, such as CPU usage or memory availability, can lead to fluctuating results. Background processes, such as updates or antivirus scans, can significantly impact the benchmark’s outcome. Furthermore, the specific benchmark tests employed and their complexity contribute to the potential for inconsistent results. The hardware’s thermal profile can also play a part, as temperature fluctuations can affect performance.
Troubleshooting Guide for Performance Problems
A systematic approach to troubleshooting performance issues is vital. This involves starting with basic checks and progressively investigating more complex scenarios. A crucial initial step is to review system logs for error messages, which may provide clues to the root cause. Monitoring CPU and memory usage during benchmark tests or typical use can help pinpoint resource bottlenecks.
Identifying Potential Hardware Conflicts
Hardware conflicts are a common cause of performance problems. Incompatible drivers or conflicting device settings can lead to system instability and reduced performance. Carefully review device manager for any yellow exclamation marks or error messages associated with hardware components. Consider uninstalling and reinstalling drivers for suspect devices or updating to the latest versions. Checking for device conflicts is essential for maintaining a stable and high-performing system.
Managing System Resources Effectively
Efficient management of system resources is crucial for optimizing PC performance. This involves controlling background processes, allocating resources effectively, and ensuring optimal power management settings. Closing unnecessary programs and disabling startup applications can free up system resources, leading to improved performance. Using tools to monitor resource usage and identify resource-intensive applications can help optimize the system.
Table of Common Causes and Solutions
| Common Cause | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Insufficient RAM | Upgrade RAM to meet system requirements. |
| Hard drive issues | Check hard drive health and consider upgrading to an SSD. |
| High CPU usage | Close unnecessary programs, optimize applications, or upgrade the CPU. |
| Driver issues | Update or reinstall drivers for affected devices. |
| Overheating | Ensure proper airflow and consider a cooling solution. |
| Background processes | Disable or close unnecessary background processes. |
| Malware or viruses | Run a full system scan and remove any detected threats. |
Optimizing Performance (Beyond Benchmarking)
Beyond simply benchmarking your new PC’s performance, ongoing optimization is crucial for sustained high-speed operation and tailored performance for various tasks. This involves understanding how to fine-tune your system for specific needs, such as gaming or video editing, and actively maintaining its health to prevent performance degradation over time. Proactive measures are essential to ensuring your PC consistently delivers optimal performance.Effective optimization extends beyond the initial benchmark results.
It’s a continuous process of identifying and addressing bottlenecks, fine-tuning settings, and proactively maintaining the system’s health. This approach leads to a system that not only meets your current needs but also adapts to future demands.
Power Management Settings
Power management settings can significantly impact performance. Adjusting these settings can lead to noticeable improvements or detrimental effects, depending on the use case. For example, using high-performance power plans in applications requiring significant processing power can lead to better results. However, using a high-performance plan when gaming for extended periods may lead to higher energy consumption and potentially shorter battery life.
Careful consideration of these settings is essential to achieve the desired balance.
Identifying and Removing Unnecessary Programs and Processes
Unnecessary programs and processes consume system resources, impacting performance. Identifying and removing these can lead to noticeable speed improvements. Regularly reviewing and eliminating unused applications, browser extensions, and background processes is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Tools like Task Manager provide insights into resource usage, allowing users to pinpoint and terminate non-essential processes.
Regular System Maintenance
Regular system maintenance is essential for maintaining optimal performance. This includes tasks like disk cleanup, registry defragmentation, and general system file optimization. Consistent maintenance prevents the accumulation of temporary files, cached data, and other unnecessary information that can slow down the system over time. A clean and well-maintained system is more efficient and responsive.
Updating Drivers
Updating drivers is crucial for performance improvements. Outdated drivers can lead to compatibility issues and reduced performance. Regularly checking for and installing driver updates can significantly improve system stability and functionality. Modern operating systems often include automatic driver update features, but manual checks can ensure you have the latest versions for optimal performance.
Recommended System Maintenance Tasks and Frequency
Regular maintenance tasks are critical for keeping your PC in top shape. The following table provides a guideline for recommended tasks and their frequency:
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Disk Cleanup | Weekly |
| Registry Cleaner (use with caution) | Monthly |
| Defragmentation (if needed) | Quarterly |
| Driver Updates | Bi-weekly or as needed |
| Uninstall Unused Programs | Monthly |
| File System Optimization | Quarterly |
Note: Frequency may vary depending on usage patterns and the specific needs of your system.
Optimizing for Specific Tasks
Optimizing your PC for specific tasks like gaming or video editing requires tailored strategies. For gaming, consider adjusting in-game settings for optimal performance. Reducing graphical settings or adjusting resolution can improve frame rates. For video editing, consider using specialized software tools or adjusting settings for efficiency and reducing processing time. Using dedicated graphics cards or upgrading your system’s components can also significantly improve performance for demanding tasks.
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, benchmarking your new PC provides invaluable insights into its performance characteristics. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can gain a deep understanding of your system’s strengths and weaknesses. This knowledge empowers you to optimize your PC for various tasks, from everyday use to demanding applications. This comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to fully appreciate and utilize the capabilities of your new machine.