Maintaining optimal CPU performance is crucial for any computer user. A key aspect of this maintenance is reapplying thermal paste, a crucial step to ensure proper heat dissipation. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to reapplying thermal paste, covering everything from preparation to testing and troubleshooting.
Reapplying thermal paste is essential to prevent overheating, which can lead to performance issues and even damage your computer components. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can effectively improve your CPU’s cooling and prolong its lifespan.
Introduction to Thermal Paste Reapplication

Reapplying thermal paste is a crucial maintenance step for ensuring optimal CPU performance and longevity. Over time, the thermal paste’s effectiveness diminishes, leading to a rise in CPU temperatures. This deterioration often results from the paste drying out, or becoming displaced due to component movement. Regular reapplication is vital for maintaining a consistent and efficient heat transfer pathway between the CPU and the heatsink.Thermal paste reapplication is not simply a cosmetic task; it directly impacts the CPU’s operating temperature.
A properly applied layer of thermal paste ensures efficient heat dissipation, preventing overheating and potential damage to the CPU. Common scenarios requiring reapplication include the installation of new heatsinks, after significant use, or after an upgrade or repair. Understanding the process, benefits, and required tools can significantly improve the CPU’s overall health.
Why Reapply Thermal Paste?
The effectiveness of thermal paste diminishes over time due to factors such as drying and displacement. This reduction in effectiveness can result in increased CPU temperatures, potentially impacting performance and leading to premature component failure. Regular reapplication ensures a consistent, efficient heat transfer pathway.
Common Scenarios Requiring Reapplication
Reapplication of thermal paste is necessary in several situations. A new heatsink installation requires a fresh layer to ensure maximum contact. Prolonged use of a system can lead to thermal paste degradation and the need for reapplication. Likewise, an upgrade or repair, involving the CPU or heatsink, necessitates reapplication to maintain optimal thermal performance.
Benefits of Proper Reapplication
Reapplying thermal paste yields significant benefits. A properly reapplied layer ensures optimal heat transfer, reducing the risk of overheating. This, in turn, improves the CPU’s performance and lifespan by maintaining a stable operating temperature. Avoiding overheating protects the CPU from potential damage.
Necessary Tools for Reapplication
Proper reapplication requires specific tools to ensure a clean and effective application.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Clean, lint-free cloth or microfiber towel | Essential for wiping away excess paste and ensuring a clean surface. Avoid using rough or abrasive materials. |
| New tube of thermal paste | Using a fresh tube of high-quality thermal paste is critical for optimal performance. Look for paste suitable for CPUs. |
| Small, clean spatula or plastic tool | Helpful for applying an even layer of thermal paste and spreading it smoothly. Choose a tool that won’t scratch the CPU or heatsink. |
| Tweezers (optional) | Useful for picking up small pieces of thermal paste or removing any debris. |
Preparing the Components
Properly preparing the components is crucial for a successful thermal paste reapplication. This involves safely removing the old thermal paste and meticulously cleaning both the CPU and heatsink surfaces. This meticulous preparation ensures optimal thermal contact and maximizes cooling performance. A clean surface area allows for a consistent and even application of the new thermal paste, which significantly impacts the overall efficiency of your system.Thorough cleaning and preparation are paramount for achieving the desired thermal performance.
By removing any debris or residue from the previous thermal paste application, you create a pristine surface that facilitates superior heat transfer. This contributes to a more stable and efficient cooling system.
Removing the Old Thermal Paste
Effective removal of the old thermal paste is critical to a successful reapplication. Using a suitable tool and method minimizes damage to the CPU and heatsink while ensuring thorough removal. Carefully scrape away any excess thermal paste. Avoid applying excessive pressure, which can potentially damage the CPU or heatsink.
Cleaning the CPU and Heatsink Surfaces
Cleaning the CPU and heatsink surfaces is essential for optimal thermal performance. A clean surface ensures that the new thermal paste adheres properly and maximizes heat transfer. Residue from the previous thermal paste application can hinder the effectiveness of the new thermal paste.
Cleaning Methods
Various cleaning methods are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. A gentle approach is often preferred to avoid potential damage to the delicate components.
- Isopropyl Alcohol: Isopropyl alcohol is a common cleaning agent. It effectively dissolves thermal paste residue and is relatively safe for most surfaces. Use a soft, lint-free cloth or cotton swabs to apply and wipe away the residue. A 90% to 99% concentration is typically recommended. Excessive use can damage the components if not handled carefully.
- Compressed Air: Compressed air is ideal for removing loose dust and debris from the heatsink fins. Its gentle nature minimizes the risk of scratching or damaging the surfaces. Avoid excessive pressure, which can dislodge delicate components.
- Soft Cloth/Cotton Swabs: A soft, lint-free cloth or cotton swabs can be used in conjunction with isopropyl alcohol or compressed air to clean smaller crevices and hard-to-reach areas. Using a gentle touch is crucial to prevent damage.
Things to Avoid
Adhering to these guidelines is crucial to prevent damage to your components during the cleaning process.
- Abrasive Materials: Avoid using abrasive materials, such as steel wool or scouring pads, as they can scratch the CPU and heatsink surfaces, potentially damaging the delicate components. This can also create imperfections that hinder the effectiveness of the thermal paste.
- Excessive Force: Avoid applying excessive force during the cleaning process. Excessive pressure can potentially damage the delicate surfaces of the CPU and heatsink. A gentle touch is always preferable.
- Sharp Objects: Avoid using sharp objects to scrape away thermal paste residue. This can easily damage the surface of the components. A gentle and controlled approach is essential.
- Water: Avoid using water to clean the CPU and heatsink. Water can potentially cause corrosion or damage to the electronic components. Use only isopropyl alcohol or compressed air for cleaning.
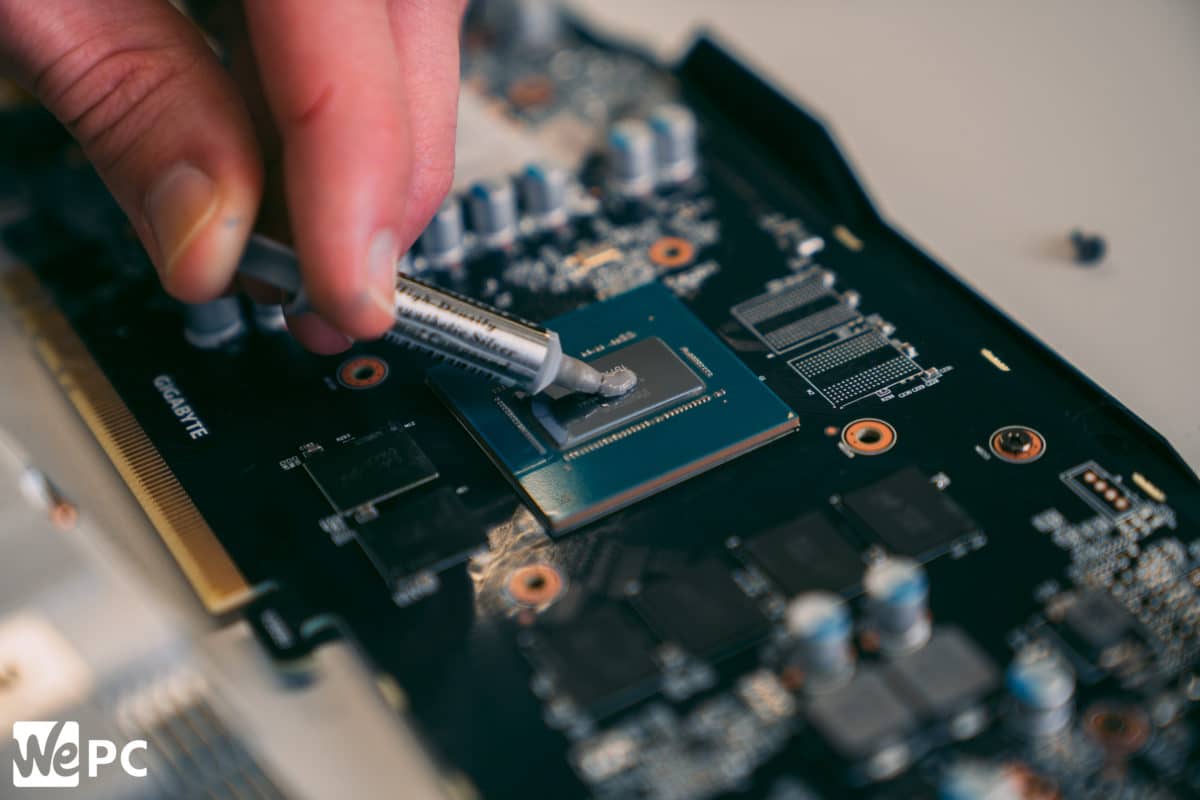
Applying the New Thermal Paste
Proper thermal paste application is crucial for optimal CPU cooling and longevity. A well-applied layer of thermal paste ensures good heat transfer between the CPU and the heat sink, preventing overheating and potential damage to the processor. Following the steps Artikeld below will help you achieve a professional-quality reapplication.
Step-by-Step Application Guide
Careful adherence to a step-by-step process is essential for successful thermal paste application. Each step contributes to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the cooling solution.
- Clean the Surface: Thoroughly clean both the CPU and the heat sink surface. Remove any dust, debris, or old thermal paste residue using a clean, lint-free cloth or a specialized cleaning kit. Ensure the surface is completely free of any foreign matter that could interfere with the paste’s adhesion and heat transfer.
- Apply a Pea-Sized Amount: Place a small, pea-sized amount of thermal paste onto the center of the CPU. A larger quantity is not required and can lead to excess paste squeezing out from under the heat sink, affecting performance. Excessive paste can also create uneven distribution and potentially damage the CPU or heat sink.
- Even Distribution: Using a clean, lint-free cloth, gently spread the thermal paste evenly across the CPU surface. Apply consistent pressure to ensure uniform coverage, avoiding any uneven patches or excessive buildup. A smooth and even layer ensures optimal heat dissipation.
- Install the Heat Sink: Carefully align the heat sink with the CPU, ensuring proper seating. Apply gentle, even pressure to install the heat sink, avoiding any twisting or tilting motions that could damage the CPU or heat sink.
- Secure the Heat Sink: Secure the heat sink using the appropriate mounting screws or clips. Make sure all mounting points are properly engaged to prevent movement or shifting during operation.
- Verify Installation: After installation, double-check the heat sink for proper seating and stability. Ensure that no components are loose or improperly aligned, which could compromise the cooling performance.
Correct Amount of Paste
The correct amount of thermal paste is critical for optimal performance. Using too little paste can reduce heat transfer, while excessive amounts can result in uneven distribution and potential leakage beneath the heat sink.
A pea-sized amount of thermal paste is generally sufficient for most CPUs. Experimentation may be needed to determine the optimal amount for your specific CPU and heat sink combination.
Importance of Even Distribution
Even distribution of thermal paste is vital for maximizing heat transfer. Uneven distribution can create hot spots, leading to overheating and potentially damaging the CPU.
A smooth, even layer ensures that the thermal paste makes contact with the entire surface area of the CPU and the heat sink. This consistent contact promotes efficient heat dissipation, keeping the CPU at a safe operating temperature.
Avoiding Air Bubbles
Air bubbles trapped beneath the heat sink during application can significantly reduce thermal conductivity, leading to reduced cooling performance. The presence of air pockets disrupts the thermal contact between the CPU and the heat sink, hindering the transfer of heat away from the CPU.
Avoid using excessive pressure or forceful spreading when applying the paste. A gentle, controlled application helps to minimize the risk of introducing air bubbles. If bubbles appear during application, gently use a clean, lint-free cloth to remove them before installation of the heat sink.
Thermal Paste Application Methods
Different methods can be used for applying thermal paste, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods can help users choose the most suitable approach for their needs.
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Application | Applying paste directly onto the CPU using a finger or applicator tool. | Simple and quick. | Risk of uneven distribution and air bubbles. |
| Spreading with Cloth | Using a clean, lint-free cloth to spread the paste evenly. | Easy to achieve even distribution. | Requires more precision and practice. |
| Using a Small Spatula | Employing a small, flat spatula to distribute the paste. | Excellent control over the amount and distribution. | Requires more time and effort compared to other methods. |
Securing the Heatsink
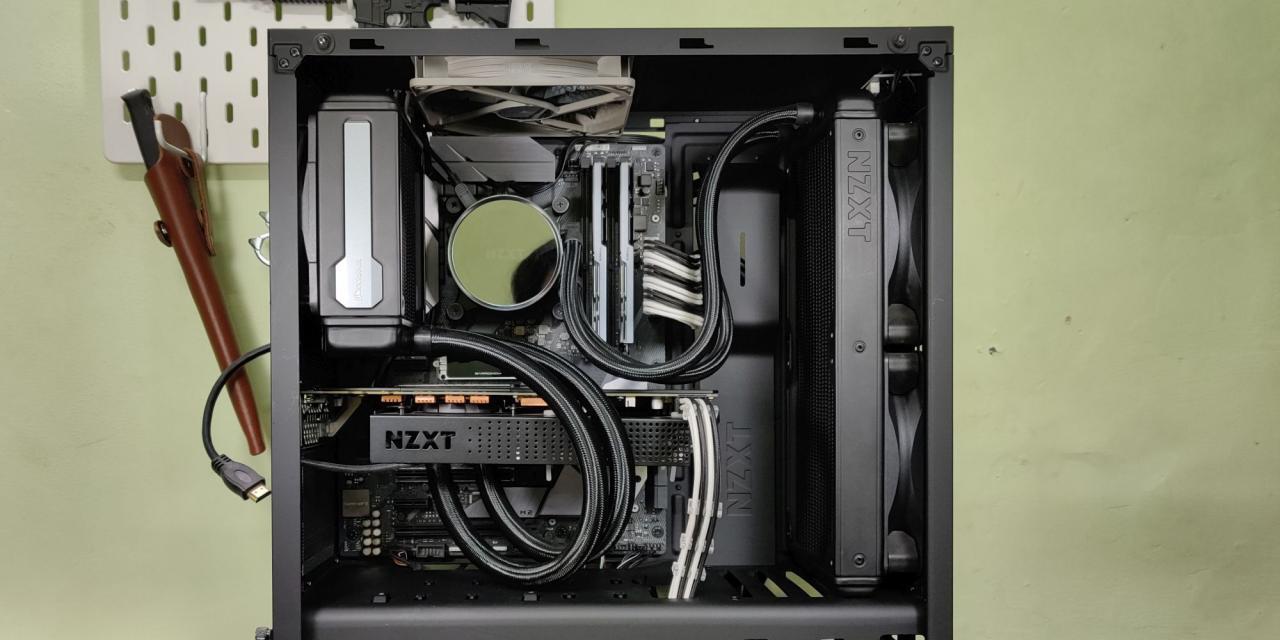

Properly securing the heatsink is crucial for efficient heat dissipation and preventing thermal throttling. Incorrect mounting can lead to uneven pressure distribution, poor thermal contact, and ultimately, reduced performance or damage to the CPU and heatsink. Careful attention to detail in this step is vital for optimal system longevity and stability.Ensuring a secure and stable heatsink installation is paramount.
A well-applied thermal paste and a correctly mounted heatsink are essential for optimal CPU cooling. This section details the process and important considerations for securing the heatsink to the CPU.
Heatsink Mounting Procedures
Different heatsinks employ various mounting methods. Understanding the specific instructions provided with your particular heatsink is critical. Adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines ensures proper installation and maximizes the heatsink’s cooling potential. Common methods include using screws, clips, or levers, each requiring specific torque or pressure to ensure adequate contact.
Importance of Correct Pressure and Alignment
Uniform pressure across the heatsink’s surface is critical for optimal thermal contact. Uneven pressure can result in hot spots on the CPU, hindering effective heat dissipation. Proper alignment is also essential, as misalignment can create gaps that reduce the effectiveness of the thermal paste and diminish the heatsink’s cooling capabilities. This alignment prevents air pockets from forming between the heatsink and the CPU, which are significant thermal insulators.
Different Heatsink Mounting Methods
Various heatsink mounting methods exist, each with its own characteristics and benefits. The most common methods include screw-on, clip-on, and lever-based mounting systems. Screw-on systems provide a more secure and robust mounting, but require precise torque to avoid over-tightening and damaging the CPU or heatsink. Clip-on systems are often easier to install but may not offer the same level of clamping force.
Lever-based systems generally provide a balance between ease of installation and secure mounting. The selection of the appropriate method depends on the specific heatsink design and the user’s familiarity with the process.
Troubleshooting Common Mounting Issues
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution ||—|—|—|| Heatsink not securely mounted | Insufficient tightening of mounting screws, improper use of clips or levers. | Re-check manufacturer’s instructions for correct torque specifications and secure the mounting mechanism accordingly. || Uneven pressure on the CPU | Incorrect alignment of the heatsink, insufficient thermal paste application. | Recheck alignment and ensure even thermal paste distribution.
Use a flat surface to check for alignment, or consult the heatsink manual. || Air bubbles trapped under the heatsink | Insufficient thermal paste application, uneven pressure, or improper mounting alignment. | Re-apply thermal paste and ensure the heatsink is correctly aligned and pressed firmly against the CPU. Consider using a thermal paste applicator to apply the thermal paste evenly.
|| Excessive pressure on the CPU | Over-tightening of mounting screws or clips. | Reduce pressure by slightly loosening the mounting screws or adjusting the clips to achieve proper clamping force. |
Testing and Verification
Proper thermal paste application is crucial for optimal CPU performance and longevity. Verification steps ensure the reapplied thermal paste is effectively transferring heat away from the processor, preventing overheating. These steps, combined with monitoring CPU temperatures and performance, help identify any potential issues early on and prevent damage to the system.Verification of thermal paste application goes beyond a visual inspection.
It involves a systematic approach to assess the effectiveness of the heat transfer, and involves meticulous monitoring of CPU temperatures and performance after reapplication.
Methods for Verifying Proper Application
Thorough verification involves more than just visually inspecting the thermal paste. Careful monitoring of CPU temperatures and performance is essential to confirm proper heat dissipation. Visual inspection, while helpful, doesn’t guarantee effective heat transfer.
Monitoring CPU Temperatures After Reapplication
Accurate monitoring of CPU temperatures after reapplication is paramount. Elevated temperatures after reapplication can indicate issues with the thermal paste application, the heatsink’s contact with the CPU, or other factors. Monitoring tools and software provide valuable data to diagnose these issues. Monitoring provides early warning of potential problems and enables prompt corrective action.
Importance of Monitoring CPU Performance
Monitoring CPU performance after thermal paste reapplication is crucial to assess the overall impact of the new thermal paste. Performance issues might manifest as sluggishness or decreased responsiveness, signifying potential issues with the thermal paste application or other factors. This helps to ensure that the reapplication process hasn’t inadvertently impacted system stability or performance.
Tools for Checking CPU Temperature
Several tools are available to monitor CPU temperatures. These tools provide a way to track the CPU’s thermal output in real-time, helping to identify potential issues and ensure proper thermal paste application.
- System Information Tools: Many operating systems provide built-in tools for checking CPU temperatures. These tools often offer a simple overview of key system metrics, including CPU temperature. They are often integrated directly into the operating system, eliminating the need for additional software installations.
- Dedicated Monitoring Software: Specialized software programs offer more detailed and comprehensive monitoring capabilities. These programs provide graphs and charts to visualize CPU temperature fluctuations over time, offering valuable insights into the CPU’s thermal behavior. Examples include HWMonitor, Core Temp, and others, enabling users to track temperature trends and potential issues more effectively.
- Hardware Monitoring Utilities: Motherboard manufacturers often include dedicated utilities that allow monitoring of system hardware components, including CPU temperature. These utilities are often bundled with the motherboard’s drivers, offering a convenient way to track critical system metrics. Such utilities frequently provide real-time graphs and historical data, aiding in troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Reapplying thermal paste is a crucial step in maintaining optimal CPU performance and preventing overheating. However, issues can sometimes arise. Thorough troubleshooting is essential to identify and rectify any problems encountered during or after reapplication. This section details common issues and their solutions.Proper thermal paste application is critical for effective heat dissipation. Issues such as uneven heat distribution or poor CPU performance can stem from inadequate paste application, improper heatsink seating, or other factors.
Diagnosing and resolving these problems will ensure optimal cooling and long-term system health.
Uneven Heat Distribution
Improper thermal paste application often leads to uneven heat distribution across the CPU. This can result in localized overheating, even if the overall temperature remains within acceptable limits. This is a critical issue to address as it can lead to thermal throttling and performance degradation. Several factors can contribute to uneven distribution.
- Insufficient thermal paste: Applying too little paste can leave gaps, preventing proper contact between the CPU and heatsink. Applying a sufficient amount of paste, ensuring even coverage, is crucial. This ensures the paste adequately fills the microscopic surface irregularities and provides thermal bridging.
- Uneven paste application: Applying paste in a thick, uneven layer or in streaks can lead to poor thermal contact. Apply a very thin, even layer of thermal paste, focusing on covering the entire CPU surface uniformly.
- Incorrect heatsink pressure: Insufficient or excessive pressure when seating the heatsink can also contribute to uneven heat distribution. Ensure the heatsink is firmly and evenly pressed against the CPU to maximize contact and minimize air pockets.
Poor CPU Performance After Reapplication
After reapplying thermal paste, if the CPU performance is noticeably degraded, various issues might be at play. Thorough diagnosis is essential to pinpoint the root cause.
- Insufficient cooling: If the heatsink is not providing adequate cooling, the CPU will overheat, leading to throttling and reduced performance. Ensure the heatsink is compatible with the CPU and properly installed.
- Driver issues: Outdated or corrupted drivers can impact performance, including CPU performance. Ensure the latest drivers for the system components are installed.
- Other system issues: System resource issues, such as high disk activity, or excessive background processes, can lead to performance degradation, independent of the CPU’s thermal state. Ensure that the system resources are not overloaded.
Diagnosing Overheating Issues
Overheating can manifest in various ways, from system instability to complete crashes. Early detection and diagnosis are crucial.
- Monitoring tools: Utilizing monitoring tools can reveal the CPU temperature and other metrics. These tools allow real-time monitoring of CPU temperatures during various tasks, helping to identify potential hotspots or sustained high temperatures.
- System instability: Random system crashes, freezes, or unusual behavior can indicate overheating. Pay close attention to any unusual system behavior.
- Software warnings: Some software might display warnings or alerts related to CPU temperatures, indicating a potential overheating issue. Actively monitor for any such warnings.
Troubleshooting Table
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Uneven heat distribution | Insufficient paste, uneven application, incorrect heatsink pressure | Apply a thin, even layer of paste; ensure even pressure on the heatsink. |
| Poor CPU performance | Insufficient cooling, driver issues, system resource issues | Verify heatsink compatibility; update drivers; optimize system resources. |
| Overheating | Insufficient cooling, blocked airflow, thermal paste issues | Ensure adequate airflow; check thermal paste application; consider additional cooling solutions. |
Advanced Techniques (Optional)
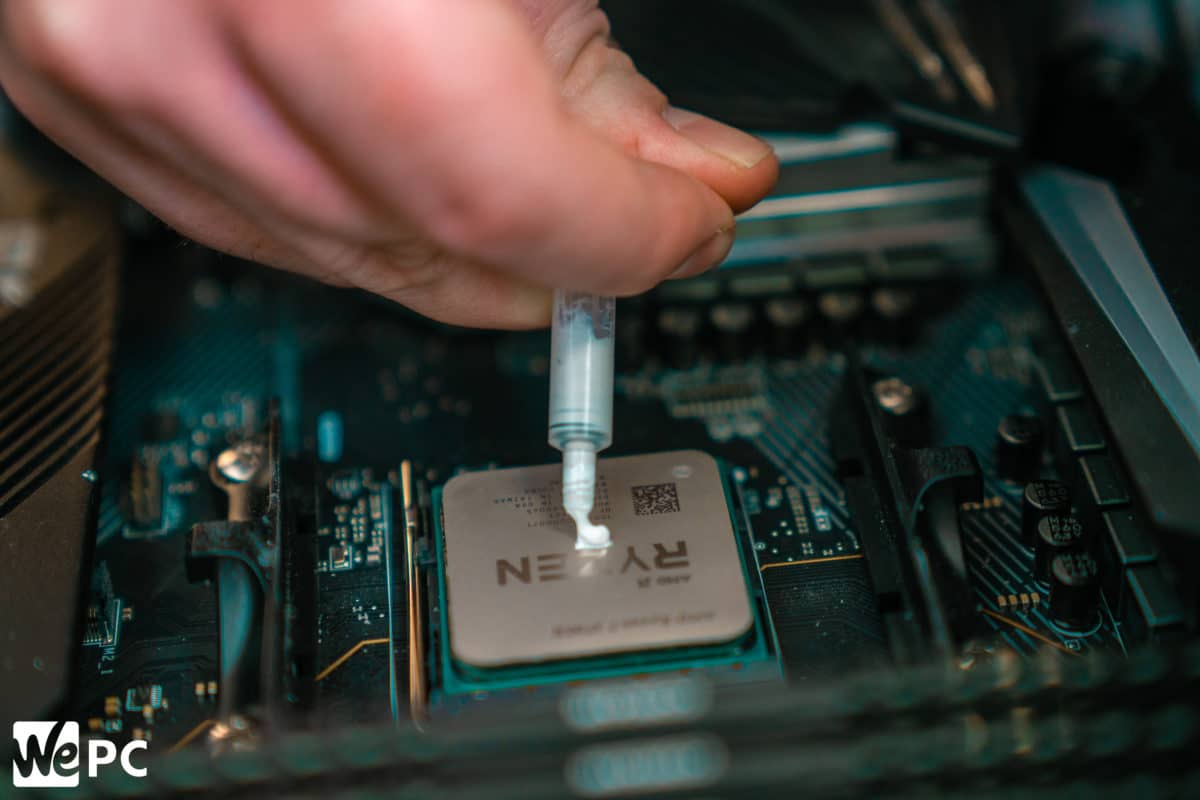

Reapplying thermal paste effectively can significantly enhance your CPU’s cooling performance. Beyond the basic steps, several advanced techniques can optimize heat dissipation and prolong the lifespan of your components. These techniques often involve a deeper understanding of the properties of different thermal pastes and the nuances of application.Choosing the right thermal paste and applying it correctly are critical for achieving optimal cooling.
Advanced techniques, while not strictly necessary for most users, can unlock further performance gains for those seeking the highest possible cooling efficiency.
Thermal Paste Types and Properties
Different thermal pastes exhibit varying properties that influence their performance in different scenarios. Understanding these properties helps in selecting the appropriate paste for your specific needs. These properties include thermal conductivity, viscosity, and consistency.
- Thermal Conductivity: This crucial property measures a material’s ability to transfer heat. Higher thermal conductivity translates to faster heat dissipation. Pastes with higher conductivity will generally provide better cooling performance.
- Viscosity: Viscosity refers to the paste’s resistance to flow. A paste with low viscosity spreads more easily, allowing for more uniform coverage and preventing the formation of air pockets.
- Consistency: Consistency, along with viscosity, determines the ease of application and spread. Some pastes are thicker, requiring more care in application, while others are thinner, offering greater flexibility.
Choosing the Right Thermal Paste
The selection of thermal paste is a critical aspect of achieving optimal cooling. Factors such as the CPU’s design, the heatsink’s surface area, and the ambient temperature should be considered when making your choice. A poor choice of thermal paste can lead to overheating and reduced system performance.
Comparison of Thermal Paste Brands
| Brand | Type | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Arctic MX-4 | High-performance | Excellent thermal conductivity, low viscosity, easy to apply, suitable for most modern CPUs and heatsinks. |
| Noctua NT-H1 | High-performance | Exceptional thermal conductivity, low viscosity, known for its reliability and wide compatibility. Often praised for its even spread and minimal air pockets. |
| Kryonaut | High-end | Extremely high thermal conductivity, specialized for high-end overclocking or high-performance systems. May be more challenging to apply evenly. |
| Thermal Grizzly Kryonaut | High-end | Exceptional thermal conductivity, very low viscosity, and excellent heat dissipation. |
Note: The table above provides a general overview. Specific features and properties may vary slightly between different batches and versions of the same thermal paste. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for detailed information.
Preventing Future Issues
Maintaining optimal CPU cooling is crucial for the longevity and performance of your computer. Regular maintenance, including reapplying thermal paste, is a key aspect of this. Proper procedures not only enhance cooling efficiency but also prevent potential damage from overheating. By understanding the factors contributing to future issues, you can proactively safeguard your system’s health.
Maintaining Optimal CPU Cooling
Proactive measures are essential to maintain optimal CPU cooling. These involve practices beyond just reapplying thermal paste. Regular checks and proactive maintenance will ensure your CPU functions at its best for a longer time.
- Regular Dust Removal: Accumulated dust and debris significantly impede airflow around the heatsink, reducing cooling effectiveness. Regularly cleaning the heatsink and surrounding components ensures optimal airflow. This simple practice can prevent overheating and maintain a healthy operating temperature. Dust buildup is a significant contributor to overheating and should be addressed regularly.
- Monitoring System Temperatures: Utilizing monitoring software allows you to track CPU temperatures in real-time. This provides valuable insight into the system’s thermal performance under various workloads. Identifying patterns and trends can help you proactively address potential issues before they escalate. For example, if you notice a sudden spike in CPU temperature during specific tasks, it could indicate an airflow obstruction or a failing component.
Regular monitoring enables timely intervention and prevents overheating damage.
- Adjusting Fan Speeds (if applicable): If your system has adjustable fan speeds, fine-tuning them can optimize cooling. Higher fan speeds provide better cooling during intensive tasks. Conversely, lower speeds might be sufficient during idle periods, thus improving energy efficiency. Proper fan speed adjustments ensure the CPU remains at a comfortable temperature while also conserving energy.
Importance of Regular Thermal Paste Checks
Regularly inspecting the thermal paste’s condition is vital for maintaining optimal CPU cooling. Thermal paste degradation can reduce the effectiveness of heat transfer, leading to overheating.
- Visual Inspection: Visually inspect the thermal paste for signs of dryness, cracking, or excessive buildup. A thin, even layer of thermal paste is ideal. If the paste appears dry, uneven, or cracked, it’s a strong indicator of reduced performance. This simple visual inspection is a crucial step in preventing overheating.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitoring CPU temperatures while performing various tasks can reveal the need for reapplication. High temperatures during light tasks or consistent high temperatures during demanding tasks often point to thermal paste degradation and warrant reapplication. This data-driven approach allows you to anticipate issues and maintain optimal cooling.
Lifespan of Thermal Paste
Thermal paste has a limited lifespan. Over time, the paste can dry out or lose its effectiveness. This is a critical factor in ensuring long-term CPU cooling performance.
- Typical Lifespan: The lifespan of thermal paste can vary depending on factors like usage and environmental conditions. However, a general guideline is 2-5 years for optimal performance. The typical lifespan of thermal paste is influenced by factors like operating temperature and usage intensity.
- Predicting Needs: Regular temperature monitoring can help predict the need for reapplication. If you notice a gradual increase in CPU temperatures, it’s a clear sign that the thermal paste may be nearing the end of its lifespan and a reapplication is necessary. Regular monitoring and reapplication when necessary ensure long-term cooling performance.
Best Practices for Avoiding Overheating
Implementing best practices can significantly reduce the risk of overheating. Overheating is a significant concern for CPU performance and longevity.
- Choosing a Suitable Heatsink: Select a heatsink that is compatible with your CPU and adequately sized to dissipate heat effectively. The proper heatsink selection is crucial in preventing overheating.
- Avoiding Excessive Overclocking: Refrain from overclocking beyond the CPU’s recommended limits. Overclocking can generate excess heat, potentially leading to overheating and damage. Overclocking can put significant stress on the CPU and heatsink, necessitating careful monitoring and preventative measures.
Closing Summary

In conclusion, reapplying thermal paste is a straightforward process that can significantly improve your CPU’s cooling and overall performance. By following this guide’s detailed steps, you can ensure proper heat dissipation and avoid potential overheating issues. Remember to prioritize safety, accuracy, and thoroughness throughout the process.
Properly reapplying thermal paste is an important aspect of computer maintenance. This guide has provided a clear and detailed explanation of the process, enabling you to confidently handle this task yourself.